Advanced Manufacturing Roadmap
What are the guidelines that support this research project?
This summary is based on Helwig and Goldman (2024), and is intended to enhance my writing skills, business analysis, and process improvement capabilities for the U.S. market.
The texts may contain typos and incomplete thoughts and will undergo continuous revision and development. In addition to the main document, I’ve also used reference materials such as documents, books, videos, and articles to support this work.
Advanced Manufacturing
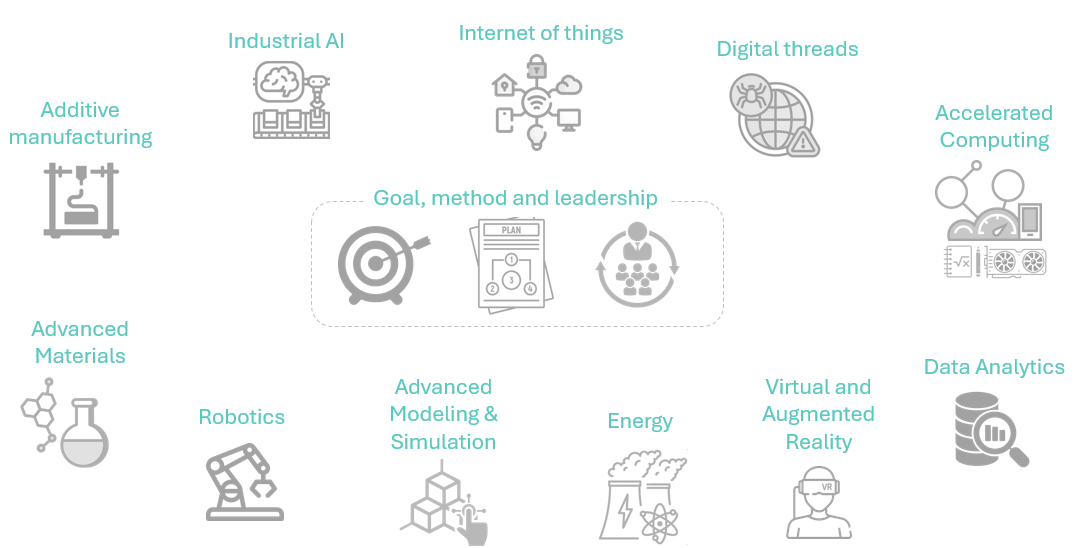
- Advanced manufacturing refers to the use of innovative technologies, processes, and methods(e.g. intelligent robotics, additive manufacturing, digital twins, artificial intelligence, and lean principles) to accelerate the design and production of physical goods. This approach anables scalability and capabilities that were previously impossible, including cost reduction and creating of value-added products in shorter production cycles.
Digital twin is a virtual model of a physical object, product, process, or system that is regularly updated with data to maintain a strong resemblance to its real-world counterpart.
Think of it like a very detailed, always-on simulation(e.g., if you have a physical machine on a factory floor, its digital twn would be a software mdoel taht gets constant updates from sensors on the real machine. This allows you to monitor, analyze, and event predict the behavior of the physical assent without directly interacting with it)
- Advanced manufacturing integrates human expertise with automation, robotics, AI(e.g, machine learning, large language models, computer vision, autonomous agents), the Internet of Things(IoT), and 3D printing to drive innovation and operational efficiency.
Impacts
Advanced manufacturing promotes economic stability, enhances competitiveness, and drives growth, while preserving essential workforce skills and reducing market risks. Key impacts include:
- National Security: A strong manufacturing sector is vital for economic independence and national security. By producing essential goods domestically, the U.S. can reduce reliance on foreign powers.
- Productivity: Streamline production processes by automation, reducing cycle times and labor cost.
- Costs: By optimizing processes and reducing waste.
- Supply Chain: IoT and data analytics can improve visibility and efficiency, reducing lead times and inventory costs.
- Jobs and skill requirements: New opportunities in fields like robotics programming, data analysis, and maintenance of advanced machinery.
- Quality: High precision, uniformity and consistency in production.
- Customization and Flexibility: 3D printing enable on-demand manufacturing of highly customizable products without retooling.
- Environmental Impact: By reducing material waste, energy consumption, and gas emissions.
The Past
Exploring past experiences stimulates our capacity for mental time travel, which is essential for survival and adaptation. It helps us predict outcomes, learn from mistakes, and develop a sense of identity. Studying the past also reveals how experiences shape history and influence memory formation and learning.
Process Innovation History
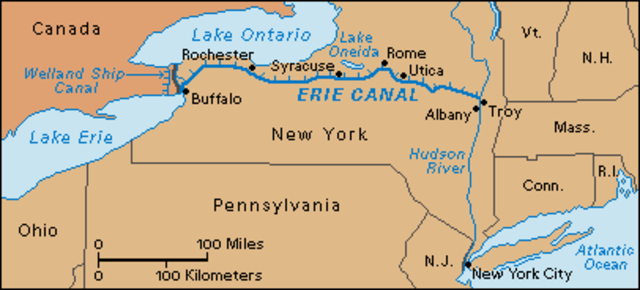
Shortening the Distance: Improving the movement of goods to stimulate trade, industry, agriculture, and communication both regionally and nationwide. The Erie Canal(a navigable waterway completed in 1825), connected the Great Lakes to the Atlantic Ocean, according to DPLA (1821). Its primary goal was to develop and agricultural expansion. This transformation significantly impacted the marginal product of labor, as noted by Kaiman, Vandenbroucke, and Wolla (2024). Beyond its economic effects, the canal had profound societal impacts, shaping the nation’s development throughout the 19th century:
- It spurred westward migration and enhanced commercial trade between regions.
- It contributed to the emergence of new towns along its route.
- It fostered cultural and political unity between the Northeast and the expanding Western territories.
- It spurred westward migration and enhanced commercial trade between regions.

New Processes: Creating better products, faster and more affordably. The Bessemer process patented by Henry Bessemer in 1855 in the U.S. and popularized in the 1870s by visionary entrepreneur Andrew Carnegie. This innovation enabled the construction of transformative infrastructure such as bridges, ships, trains, elevators, oil and water pipelins, and vertical buildings. The process dramatically reduced the manufacturing time of single steel rail from two weeks to just fifteen minutes.
Knowledge Base, Science, and Data: During the rise of the oil industry in the late 19th century, improvements in efficiency within the petroleum refining process were crucial to gaining a competitive edge. These advancements were achieved through the application of scientific methods, the establishment of strategic commercial partnerships. and the implementation of product standardization and operational uniformity. Together, these innovations not only streamlined production and reduced costs but also reinforced John D. Rockefeller’s natural leadership capabilities, enabling him to build a highly organized and dominant enterprise in the energy sector.
Redefine Customer Values: Companies like Ford, Home Depot, Nike, Dell, Apple, Netflix, and Tesla exemplify how redefining customer value can unlock entirely new demand. Rather than competing solely on price or features, these companies intruduced experiences and solutions that consumers didn’t even know they needed and tranforming industries in the process. By building powerful, cohesive business systems designed to consistently deliver this new value, they outperformed competitors who were still focused on traditional efferings. As a result, the elevated customer expectations to levels that others struggle to meet, creating a lasting competitive adavantage rooted in innovation and custmer centric thinking.
Importance of competition: There is a potential link bewteen consistently low levels of stress and anxiety(especially when individuals or organizations remain in their confort zones), and a decline in economic competitiveness. While operating within a confort zone can support mental and physical well-being, it may also foster complacency and resistance to change. In contrast, moderate stressors(**such as the presence of strong competitors or the pressure of market competition*), can stimulate problem-solving, innovation, and the adoption of new technologies. Theses challenges push individuals and organizations to adapt, evolve, and improve. Over time, a lack of competitive pressure and growth opportunities can lead to reduced motivation, diminished creativity, and stagnation. Stress, when managed effectively, acts as a catalyst for cognitive adaptation, which is essential for maintaining productivity and relevance in dynamic economic environments. Historical patterns of this bahavior were evident in the United States during 1980s, as documented by sources such as JustARandomChannel (2019), Peter Santenello (2024), and FRONTLINE PBS (2024), and similar trends are observable in Germany in 2024, as reported by DW News (2024). These examples highlight how the absence of meaningful competition can erode a nation’s or organization’s innovative edge.
Process Improvement: Founded in 1906 by Willian Riley, New Balance is an American footwear and apparel company headquartered in Boston, Massachusetts. It is recognized as one of the world’s leading manufacturers of high-quality athletic footwear. Known for its “Made in USA” products, the company emphasizes innovation and performance, applying lean principles and tools to enhance product flow from its manufacturing plants to retailers and end customers.
New Balance began its lean transformation journey in 2003 with guidance from the Toyota Supplier Support Center. The company focused on problem-solving and process improvement to foster a culture of employee engagment while boosting operational performance.
Lean is both a management philosophy and a set of practices aimed at creating more value for customers with less waste. It emphasizes continuous process improvement and the elimination of non-value-adding activities. A deep understanding of the value creation process, ongoing learning through PDCA(Plan-Do-Check-Action) cycles, and a willingness to challenge assumptions are essential for both workers and managers. These principles not only improve efficiency but also strengthen competitiveness in a fast-changing global market.
Problem-Solving Culture A strong problem-solving culture empowers employees to actively identify and address issues rather than waiting for top-down directives. In such environments, regular team meetings are help not just to report problems, but to collaboratively explore solutions and implement improvements. Leaders shift from giving orders(e.g., Do this, do that) to facilitating ownership by saying, “Here’s the problem, here’s the gap we’re trying to close. What do you think we should do? How can I support you?”
Lean Education Associates receive structured training on lean principles, including hands-on workshops focused on waste detection and process improvement. Lean education shifts the mindset from “the manager solves problem” to “the coach develops problem-solvers.” This approach builds critical thinking, encourages ownership, and fosters an culture of continuous improvement. By learning to identify inefficiencies and propose solutions, employees become active contributors to organizational excellence. Lean thinking becomes not just a skill but a shared language for innovation and growth.
Continuous improvement Employees are encouraged to submit improvement ideas, with recognition and rewards given for successful implementations. Lean enterprises must grow not only to increase value creation but also to provide meaningful opportunities for theirs employees. By continuously improving and becoming more efficient, they can stay competitive and help secure long-term job stability for their workforce Murman (2008)
The Present
Focusing on the present helps us understand how we process information in real time, which is essential for responding quickly to stimuli and peforming daily activities with mindfulness. One of the main challenges in staying present is managing the overwhelming amount of digital and physical distractions the constantly compete for our attention.
Challenges
Disruptive technologies emerge when new ideas(or even old ones) are reimagined through integration with advanced tools like generative AI, atomic-level computer vision, and exponential computational power. These innovations challenge traditional models, unlockingcapabilities that were previously unimaginable. Embracing them is key to staying ahead in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Demographic shifts around the world: Populations are becoming older and increasingly urbanized. Below is an example of the demographic transition occuring in several countries.
- P Pencentage of the population in each group
- T Total population (in million) in each group
- AS Number of adults per senior (aged 65 and older)
- AY Number of adults per Young (aged 0-19)

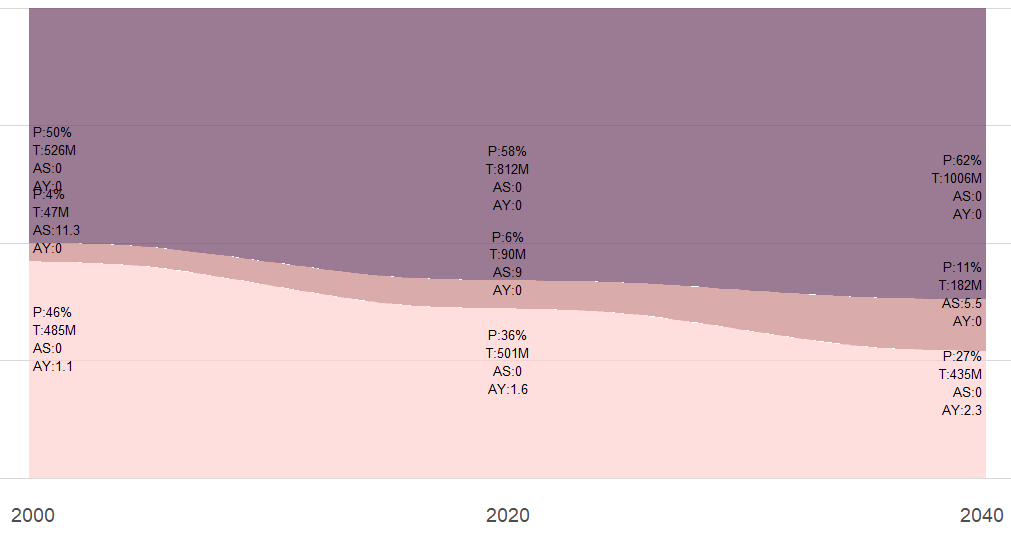
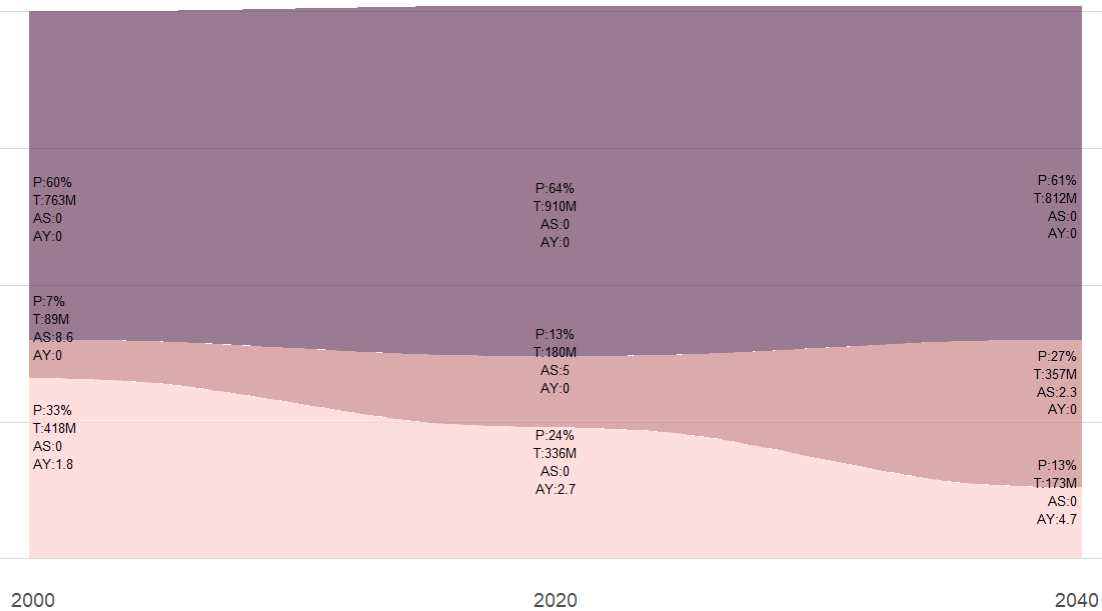
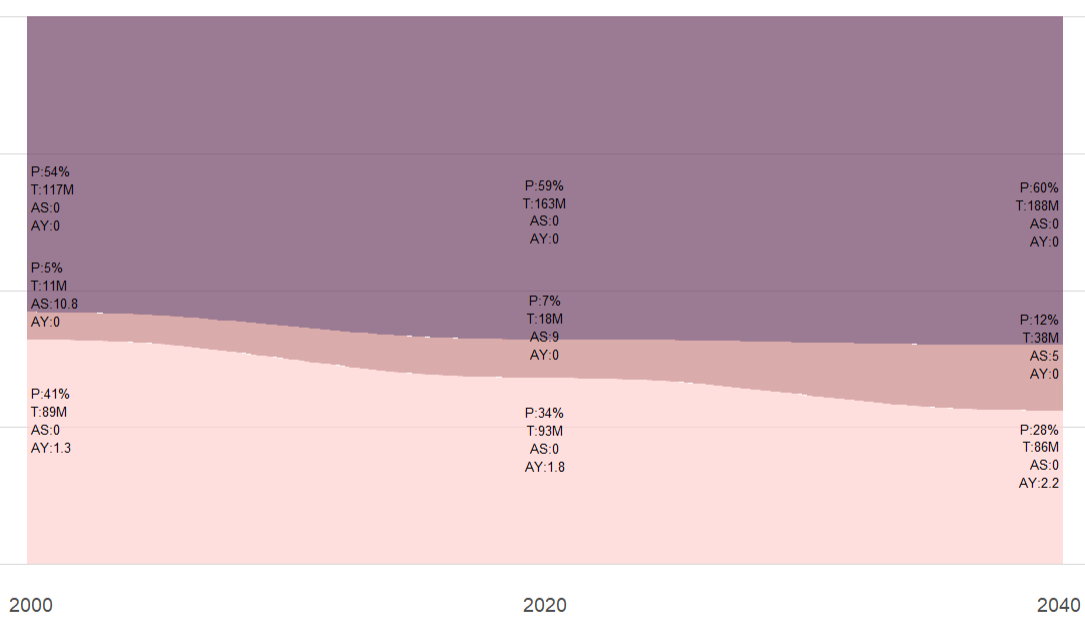
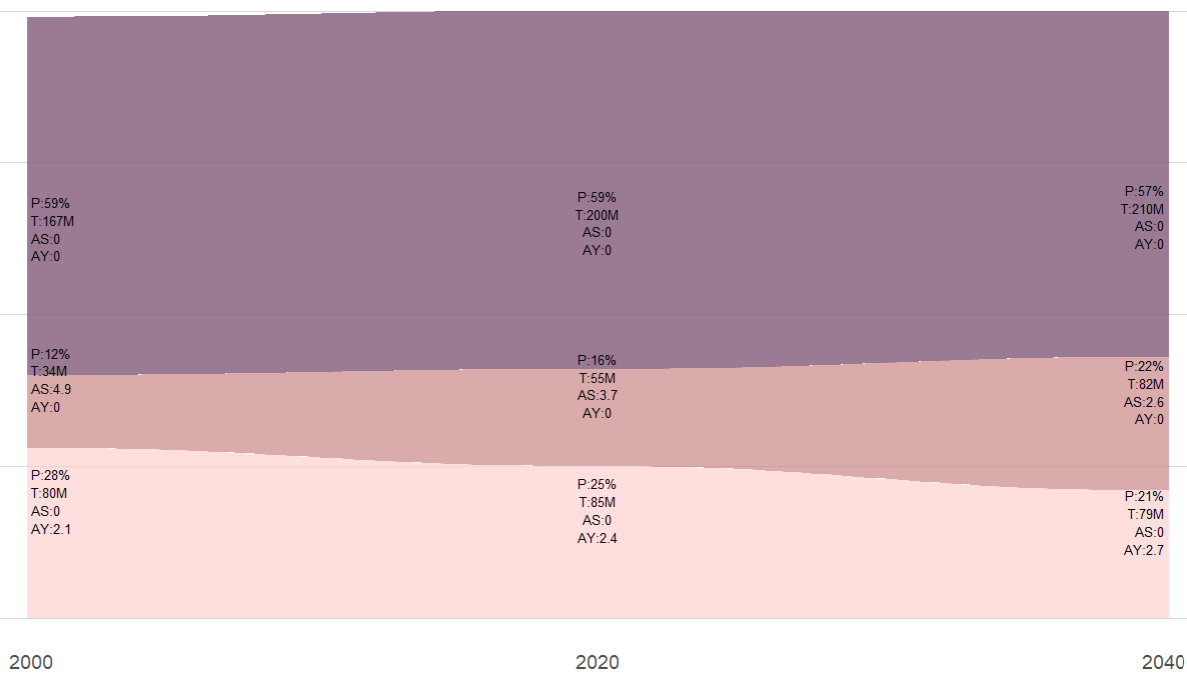
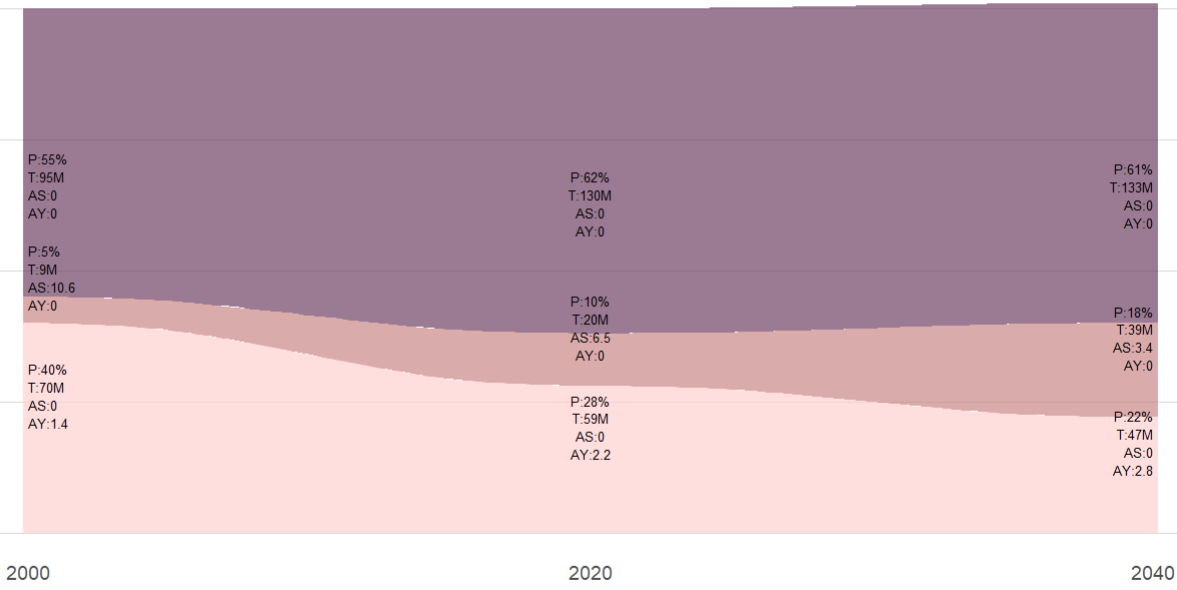
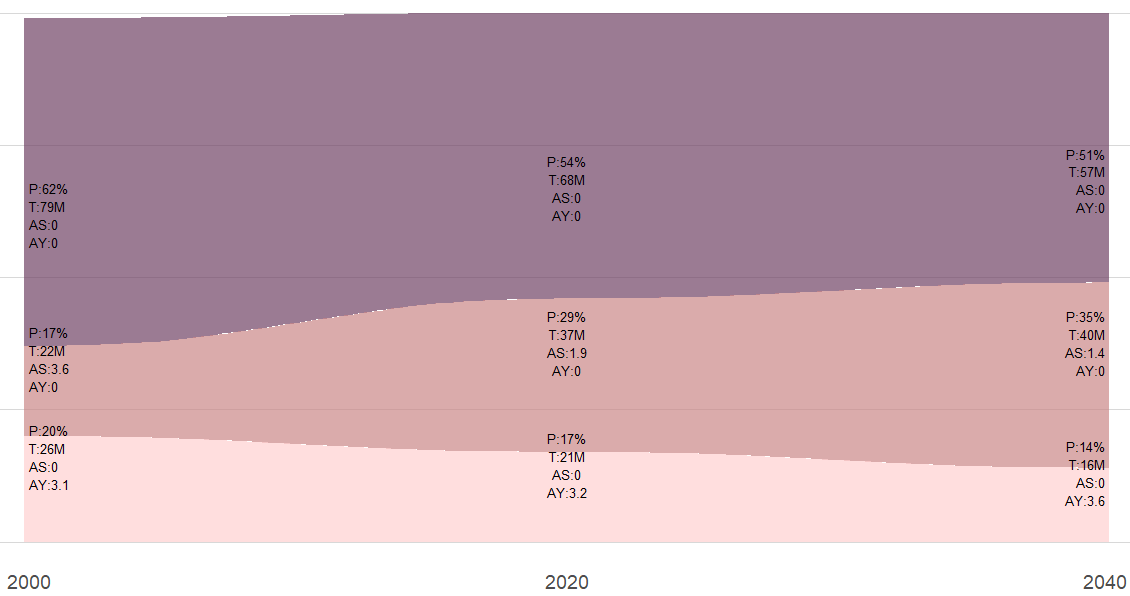
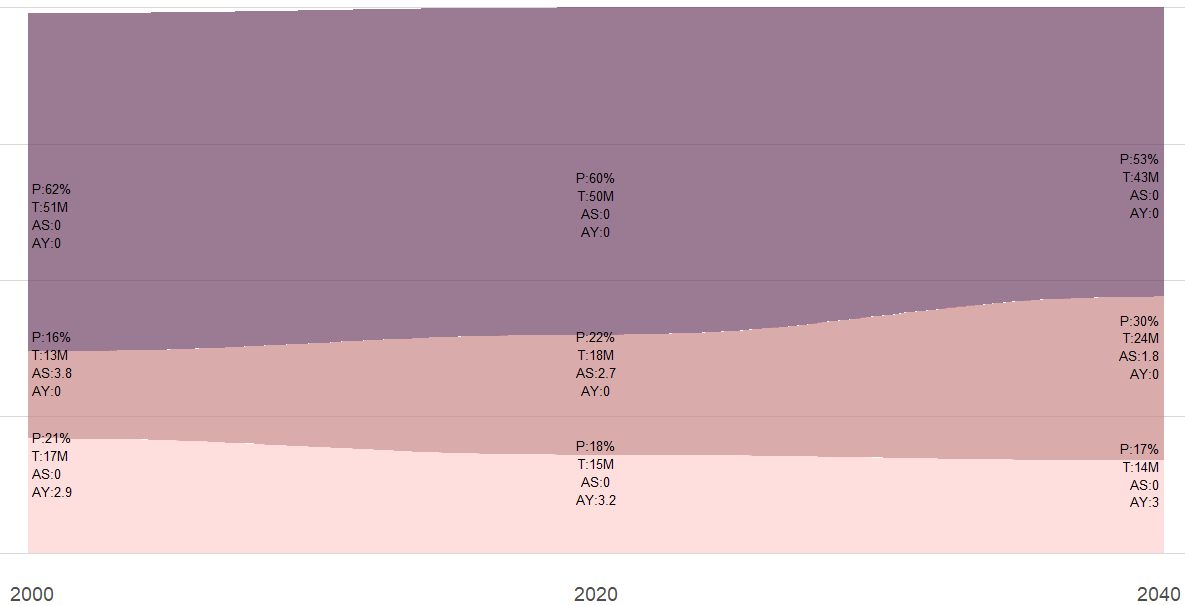
- Economic activities in emerging markets: Many countries are emerging from poverty, creating both opportunities and challenges(e.g. rising number consumer demand and increased competition due to lower labor costs).
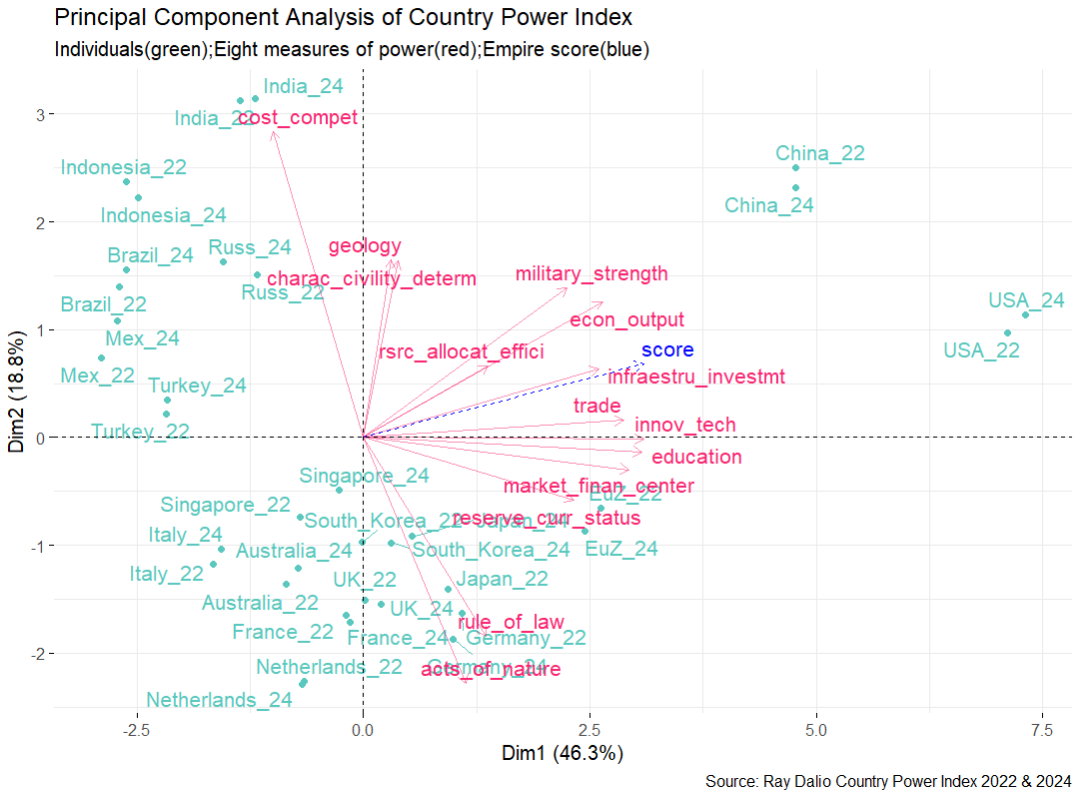
Explanation of the Principal Component Analysis (PCA) Graph of the Country Power Index
This graph you’re looking at is a “map” that helps us understand how different countries position themselves in relation to their “power” and what factors contribute to that power, for both 2022 and 2024. Think of it as a way to simplify a large amount of complex data into an easy-to-interpret image.
What are we seeing here?
- The Points (Countries): Each teal/green point represents a country in a specific year (e.g., “USA_22” is the USA in 2022, “China_24” is China in 2024). The closer these points are to each other, the more similar the countries are in their power profiles. Countries that are far apart are quite different.
- The Arrows (Power Factors): The red arrows represent the “eight measures of power” that were measured for each country (such as “military_strength,” “econ_output,” “education,” “rule_of_law,” etc.). The blue arrow (“score”) represents the total “Empire score.”
- The Axes (Dimensions): The horizontal (Dim1) and vertical (Dim2) axes are the primary “dimensions” that the PCA found to summarize all your data. Together, they explain 46.3% + 18.8% = 65.1% of the total variation in the data. This means these two axes capture most of the relevant information about country power.
How to interpret the map:
- Direction of the Arrows:
- Arrows pointing in the same direction indicate that these factors are correlated – meaning they tend to increase or decrease together. For example, “military_strength,” “econ_output,” “infraestru_investmt,” and “trade” all point in the same (upper-right) direction, suggesting that countries strong in one of these aspects tend to be strong in the others as well.
- Arrows pointing in opposite directions suggest a negative correlation. There aren’t strong examples here of directly opposing factors, which is good, as all contribute to some kind of “power.”
- The length of the arrow is important: longer arrows indicate that the factor has a greater influence on how countries are positioned on the map.
- Positioning of Countries relative to the Arrows:
- A country positioned in the same direction as an arrow (and far from the center) is strongly characterized by that factor. For example:
- USA (USA_22, USA_24) and China (China_22, China_24): They are clearly positioned in the upper-right quadrant, in the direction of factors like “military_strength,” “econ_output,” “trade,” “innov_tech,” “education,” and “infraestru_investmt.” This means these two countries are the strongest in these dimensions, which are the main drivers of the overall power “score.” They are dominating what we might call “traditional economic and military power.” The USA is positioned slightly further to the right, perhaps indicating a slightly greater strength in these aspects on average than China, but both are dominant powers.
- Nordic/European Countries (Netherland_24, France_24, Germany_22, UK_24): They tend to be in the lower quadrant, more aligned with “rule_of_law” and, to some extent, “acts_of_nature” (which could be a measure of resilience or geographic/environmental stability, or perhaps a residual measure in the model). This suggests these countries excel in governance and stability, but perhaps with less emphasis on “military_strength” compared to the USA/China.
- India (India_24) and Russia (Russ_24): Appear in the upper-left quadrant, associated with “geology” and “charac_civility_determ” (likely intrinsic or cultural characteristics influencing power, or perhaps natural resources and resilience in the case of “geology”). “India_24” also points towards “cost_compet” (cost competitiveness). This shows that their power profiles are different from the dominant powers, perhaps with more emphasis on natural resources or cultural aspects, and less alignment with the factors in the right quadrant.
- A country positioned in the same direction as an arrow (and far from the center) is strongly characterized by that factor. For example:
- Movement of Countries Over Time (2022 vs. 2024):
- You can observe how a country’s position changes from 2022 to 2024. For example, China and the USA show slight movement but maintain their dominant positions.
- Some countries might move more significantly, indicating shifts in their power profiles within just two years. For example, Turkey_22 and Turkey_24 show a slight improvement along the Dim1 axis, indicating an increase in the factors on the right side.
Business Implications:
- Identification of Competitors and Opportunities: This map allows for quick identification of the main “players” (USA, China) and an understanding of the pillars of their power. For businesses, this can pinpoint where the greatest market opportunities, innovation hubs, or geopolitical risks lie.
- Comparative Advantage Analysis: Helps understand the comparative advantages of different regions. If you are looking for markets with strong rule of law and stability, the lower quadrant might be more relevant. If you are seeking markets driven by high economic output and innovation, the upper-right quadrant is the focus.
- Location and Investment Strategies: Companies can use this type of analysis to decide where to invest, considering the power factors most important to their objectives (e.g., access to skilled labor via “education,” developed infrastructure via “infraestru_investmt”).
- Risk Assessment: Countries that move erratically on the map, or that are associated with less stable power factors, might represent higher risks or emerging opportunities.
- Understanding Trends: By comparing 2022 and 2024, we can infer global trends. If most countries are moving to the right, it might indicate a growing importance of factors associated with Dim1 (economic output, military, etc.).
- Climate change: New rules aimed at protecting the environment, enhancing our ability to adapt to and interact with it through the development of innovative products and services.
Erosion fo U.S. industrial capacity: Over the past few decades, the U.S. has experienced a significant decline in its industrial capacity. In 1980, the U.S. manufactured over 40 percent of global high-technology goods, facing 18 percent today. This decline poses a threat to both economic competitiveness and national security.
PRC’s Dominance: China has emerged as a potential competitor, cultivation substantial high-tech industrial production capacity and accounting for nearly 30 percent of global manufacturing output. China has strategically prioritized advanced manufacturing as a cornestone of its national rejuvenation strategy.
Skills Gap and Workforce Shortages: Outsourcing production has led to a skills gap in the U.S. workforce. This is compounded by a persistent labor shortage in the manufacturing sector, with a projected shortfall of 2.1 million unfilled jobs by 2030. This shortage hinders the adoption and implementation of advanced manufacturing technologies.
Small and Medium Manufacturing Adoption Barriers: Small and medium-sized manufacturers contribute the majority of the U.S. manufacturing ecosystem and they face significant obstacles in adopting advanced manufacturing technologies. These include a lacka of access to capital, expertise, and resources for system upgrades and integration.
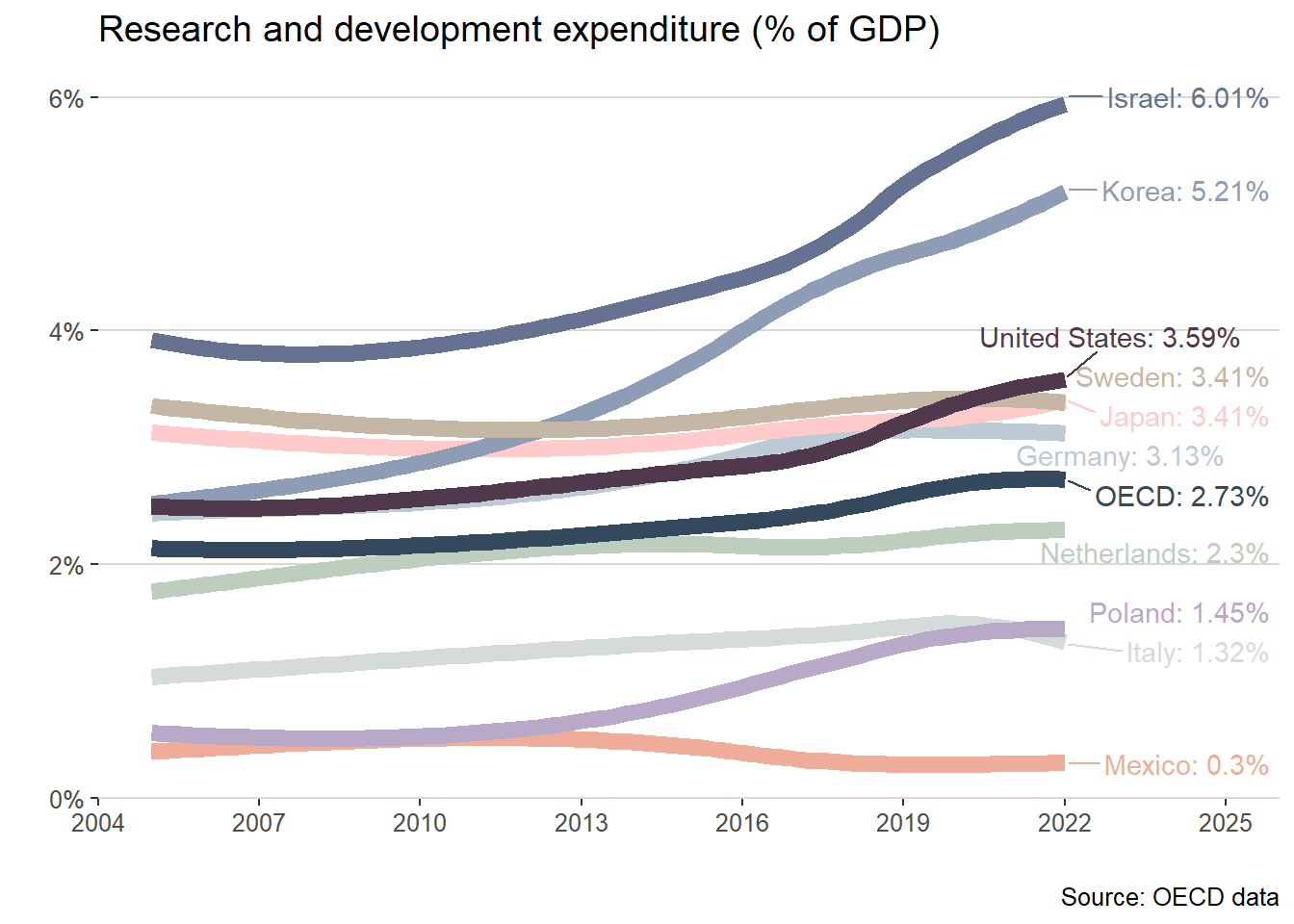
Underinvestment in R&D: The U.S. lags behind other advanced economies in manufacturing-related R&D spending as a percentage of GDP. This underinvestment hinders innovation and the development of cutting-edge manufacturing technologies. Key actors(industry, universities, and governments) need to work together.
Opportunities
- Reconceptualize the workforce: The changing nature of manufacturing requires a new approach to workforce development, with a focus on training “technologists” skilled in both engineering and operation of advanced machinery.
- Leverage existing programs: The United States can build upon succesful programs like the manufacturing USA program and the Manufacturing Externsion Partnetship(MEP) to accelerate workforce development initiatives.
- Focus on cyber skills: The increasing integration of digital technologies in manufacturing requires a workforce with strong cyber skills.
- Develop a national talent marketplace: A centralized platform connecting job seekers with advanced manufacturing opportunities can help to adress workforce shortages.
- Leveraging U.S. Strenths in AI and Software: The U.S. enjoys a significant lead in generative AI, a technology with the potential to transform various facets of advanced manufacturing (e.g.GenAI can creates copilots to helps workers interpret complex factory data and enhance AI-driven design tools that can create product designs from natural language descriptions)
- Rebuilding Domestic Production Capacity:
- Public and Private Investments:
- Collaboration with Allies and Partners:
- Reshoring and Scaling Up Production:
Industrial Policy for Process Innovation and Recent Development in U.S.
- CHIPS Act: The U.S.manufacturing share of GDP down 16% since 2012, share of semiconductor production declined from 37% in 1990 to 12% in 2022, and produced no cutting-edge advanced chips. Also, $205B trade deficit in advanced tech products, and the Hamilton Index R. D. Atkinson (2022) showing gaps with comparison to another countries. To reduce theses gaps, U.S. Congress passed Chips Act to incentivize U.S. and allied country firms to build or expand advanced-industry R&D and production sites in the United States. The focus on quantum computing, robotics, 6G equipments, gene edititing, high bandwidth memory chips, chipmaking equipment and software to develop advanced AI systems to improve manufacturing capabilities. Not only invent in U.S. but manufacture in U.S.
Science: The basic idea was to identify 10 strategic tecnologies like quantum autonomous systems, AI, biotech, etc. and then give funding to National Science Fundation but for slightly later TRL research more focus on commercialization and partnership with industry.
Regional Innovation Hubs: Program that recognized that almost all of the really advanced innovation and job growth was in five methopolitan areas in the U.S. (Silicon Valleym, Boston, Seattle) and that there was this big regional gap in the heartland if you will so this
Related Manufacturing: The manufacturing extension partnership at the National Institute of Standards and Technology it’s basically extension services for SMMs(Small and medium-sized manufacturers).
IRA(Inflation reduction Act): During the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, the U.S. has experienced 40-year record-high inflation that has just now started to cool down over the past serveral months. Inflation Reduction Act was sined into law in 2022. Key provisions of the bill are directly aimed at improving the lives of the American middle class and easing financial burdens in a post-pandemic economy. This includes up to $600 per year toward energy-efficient skylights, and up to $500 per year for two doors.
Establish an economic initiative commiting the U.S. to increase its relative level of advanced-industry concentration by 20% poonts in a decade.
According to Atkinson (2024) , Assuming a 3% growth rate in the rest of the economy, doing so could add nearly $2.5T to advanced-industry output over 10 years. It would also reduce U.S. supply chain vulnerability, create millions of good jobs, could adjust imbalances in home prices, reduce trade deficit, waken China’s advanced economy, and shore up dual-use industries critical to U.S. National Defense.
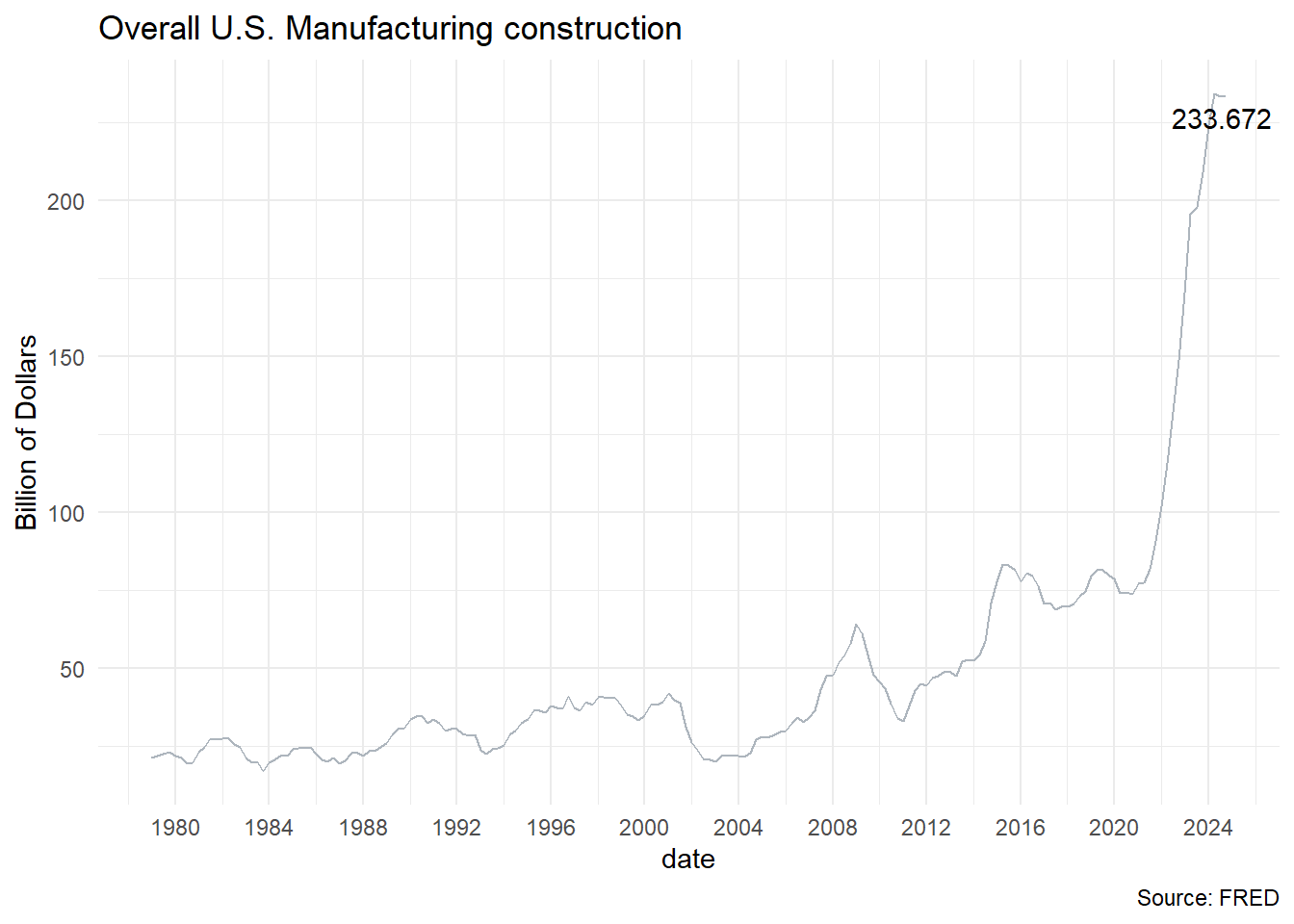
According to Bonvillian (2024) , different approaches were applied such as top down, bottom up, direct production support, demonstration projects, supply chain support, and regional implementation. The impact can be seen in the chart below (Overall U.S. Manufacturing construction), and also in the growth of investment in machinery and equipment(by brekdown of GDP).
The Future
Studying the future to understand decision-making processes, planning, and expectation building, which are crucial for strategic goals. Anticipating future scenarios helps analyze consequences and risks, leading to more effective and safer decisions. The challenges is to control anxiety especially in very optimistic or pessimistic projections.
Process Innovation of the future
Shorten the distance Improving the flow of traded goods transforming trade, industry, agriculture, and communication in the region and across the country.
Returning supersonic trips more affordable for passengers, profitable for companies, cleaner, quieter, and dramatically more fuel efficient. Speed of sound making the world feel smaller for example Tokio-Seattle in 4.4 hours, New York to London in 3.4 hours. The overture synphony engine runs with a 100% sustainable aviation fuel making supersonic flights more efficient than subsonic flights in terms of carbon emissions.
Satelite high speed internet communication More information, education,
Hyperloop is a technology has the potential to offering faster, more efficient, and sustainable logistics solutions. It can transport cargo at speeds of up to 700 mph, significantly reducing travel times, reducing downtime and incresing overall efficiency. some ot the challenges of this technology today are maintaining a vaccum seal in the tubes, propulsion, and levitation systems. Despite thise challenges, several companies, including HyperloopTT, Hardt B.V., and Transpod, are actively working on developing hyperloop technology for cargo transportation.
New processes: Making better products, faster and cheaper. (Innovation economic book here, tesla unbox here, example based tactile simulation and sim-to-real applications )
- Battery manufacturing process Advancing dry-process battery technology that enable to dry print anodes and varios cathodes(e.g lithium iron phospate-LFP, nickel manganese cobalt-NMC, sodium ion etc) with no metal or liquid inside it, saving weight(23% from today standards), space in the packaging, costs(7% from today standards), more easely to recycling, more safe because no risk of thermal runaway, and 30% more energy density(from today standards 272 Wh/kg).
Sakuú revolutionary dry-electrode printing technology enables more advanced and sustainable battery manufacturing at scale, including elimination of toxic materials and solvents, reduction in cost complexity, and ability to work with a very range of both current and future active materials and battery chemistries. It’s enable battery producers and original equipment manufacturer(OEMs) to successfully meet this incredible surge in demand and do it more sustainably. That’s why we are the world’s first manufacturing platfform for printing battery electrodes?
— Mr. Robert Bagheri, founder and CEO of Sakuú
Modular Assembly or Unboxed Manufacturing Process A modular approach where vehicle sub-assenblies are manufactured independently and connected later. Giga Castings, replacing hundreds of smaller parts with large, single-piece castings simplifies assembly, reduces weight, and improves structural rigidity. Autonomous Production eliminating traditional conveyor belts and exploring autonomous vehicles that move through production areas. Flow chart would go from a linear process flow to a parallel process flow. 30% increase in assembly speed and a 44% increase in worker density requiring a smaller factory, 40% smaller factory footprint leading to lower capital expenditure and 50% reduction in cost of good sold for future vehicles.
Knowledge base, science, and data: (insert Lip-Bu Tan here, What are the limitation of scientists today?What are your questions? Insert the schematic process of the beagle sensors and processing here )
Chip manufacturing there a five generations waves happening at the same time including AI Machine learning, Industry 4.0, Autonomous driving, and cloud computing.
Data analysis U.S. have in BLS website which has 400 digitis nakes codes manufacturing sectors with every year like productivity growth, amount of labor, labor cost, capital investment. For example use this data to correlate wage levels to capex. Does Capex correlate to lagged productivity? What sectors doing the most? Today don’t also have any analysis of the causes for example why is our car production sector so weak?
Smart grids Planning of alternatives, When increasing of distributed generation(pch, biomass, pv, nuclear, hydro, coal, o&g, vehicles) that requires a network that absorbs, knows and receives this data and reacts positively at the same time thatt is has to give a return to those who are offering energy and to those who are investing. Concepts of automation, data science, great possibilities of energy transactions.
The ability of EVs to both draw electricity from the grid for charging and supply electricity back to the grid through vehicle-to-grid(V2g) technology has a significant implications for the smart grid system. An example of a practical application of the system would be when a blizzard is forecast. Wheather forecast systems communicate with vehicles requestion maximum battery charging before the storm. This charge could be used during a period of power outages.
Real world example: Denmark’s Edison Project with V2G feasibility with 10 bi-directional EVs, Californica V2G Pilot tested this technology with 50 EVs, Japan’s Chademo Association developed V2G-capable charging standards. Future outlook is increase adoption, advanced technologies(improvements in battery tech, power electronics and cybersecurity), and grid integration(decentralized renewable energy-based smart grid).Nuclear Fusion Bring electricity to low income countries bringing significant improvement in standard of living.
Smart cars Communication between them and the system reducing accidents and casualties, saving millions of dollars and thousands of lives.
Smart tags Solving the problems of lines in the supermarket.
High speed trains Solving problems of wating times and necessity of security checks in the airports.
Smart robots machine-knitted pressure-sensitive low cost tactile skin that is scalable
Autonomous truck John Deer CES 2025, save time, reduce risks os crash through drive assistant. 20 years ago we were probably pushing 120 tons an hour, and today we’re mining 350/370 tons an hour. We run 24/7 we run like on a four shift basis the larg of the corry that there’s many new challenges safy, employment and training finding skilled labor is very challenging it to be able to run and see them as machine and be able operate it from my desk will eliminate the training, eliminate safety factors you want everybody to go home safe it’s going to increse productivity out of the mine and give me more time to be more creative of what we need to do in the future.
Example fully autonomous ADT or Dusty manufacture in Devenport Iowa that machine leverages starts with hihg performance eletronics, designed and tested by John Deere for over 30 years to operate in Earth’s toughest environments the ruggedized component stack includes satellite internet advanced controls, starfire gps, 360 view cameras and sensors, and high performance GPU’s which enable us to deliver real autonomy into the and dirty world of construction.Technical training Hands-on practical experience by using virtual reality and advanced training simulators to prepare the workforce for advanced manufacturing jobs (e.g Palette Skils, Advanced Industry Training by Weber State University)
Redefine customer values: Create new damand by delivering a previously unknown experience to consumers. They built powerful, cohesive business systems that could deliver more of this value than their competitors. They raised customer expectations beyond what their competitors could reach. According to Gary Cohn, increase in GDP growth could substantially reduce debt/GDP ratio, which could consequently improve investors’s long-term planning.
Process improvement: The best possible products at the lowest possible cost, in the most timely manner, on a stable long-term basis.
- Intelligent management grid Electric vehicle charging management according to variables such as demand, time, and avaiability. The vehicle would make the decision based on data analysis with focus on system avaiability.
[The main problem
Understand how innovation systems work and how to optimize their organization to drive economic growth and solve societal problems.
Attempt to get inside that unexplained or poorly understood process of innovation, that it’s like a mystery box where you know what goes in(investment, research) and what comes out(new technologies, economic growth), but also understand the internal workings of how it transforms inputs into outputs. Understand how the innovation system is actually organized to optimize the results.
History
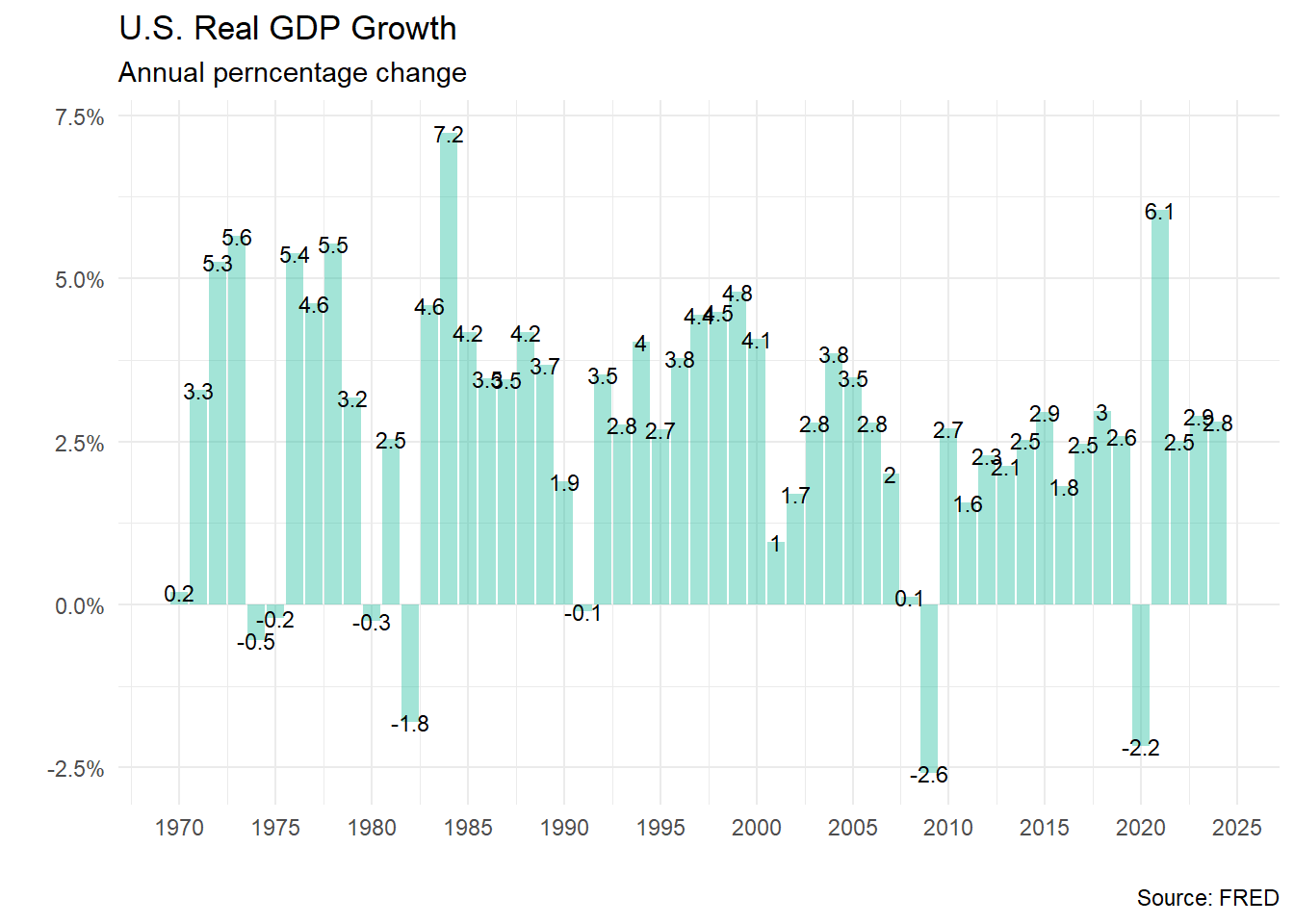
- 1945 to 1973: U.S. productivity growth 2% range.
- 1973 to 1993: U.S. productivity growth < 1% range.
- 1995 to 2000: U.S. productivity growth 3.5% and economic growth 4.2%
According to (bonvillian?) the Jorgenson’s theory shows how the IT wave of the 1990s drove significant economic growth due to rapid technological innovation. This was characterized by a core technology(semiconductors) that became ever more capable at ever lower cost.
In modern times, we could observe a similar pattern in the advancement and widespread adoption of renewable energy technologies, and advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies.
Core Technology: AI Algorithms, machine learning models, and the specialized hardware that power them.
Declining Cost Base: The cost of processing power and data representation and storage needed for AI development has singificantly decreased over time. This makes AI development and deployment better, faster and cheaper.
Increased Capability: AI models are constantly becoming fmore sophisticated, capable of handling complex tasks from natural language processing to image recognition and predictive analytics with increasing accuracy and speed.
Economic Impact: This has led to widespread adoption across various industries, from healthcare and finance to manufacturing and entertainment, driving efficiency gains, creating new services, and fostering economic growth in the digital economy.
Action Plan
- Semiconductors: Chips and Science Act, focus on increasing US competitiveness in the semiconductor industry, incentive for creating research and development centers in semiconductor techonologies.
- Energy Technologies: Inflation Reduction Act, incentives for the production of electric vehicles, batteries electricity, and tax credits for companies investing in clean technologies.
- Technology Demonstrations: Infraestructure Act, focus on infrastructure projects that promote innovation and sustainability, incentives for the adoption of clean and efficient techonologies in infrastructure project.
- 3-3-3 plan: Involve cutting the budget deficit to 3% of GDP by 2028, boosting GDP growth to 3% through deregulation and other pro-growth policies, and increasing U.S. energy production to the equivalent of an additional 3 million barrels of oil per day.
- Workforce Education:
- Ambitious of industrialize: Build the factories, Supply chain, and vertically integrate those Supply chains together.
Challenges
Learning by doing: When companies or countries cease production something, it becomes difficult to redevelop that capability. This is due to the speciallized process knowledge required to manufacture high-value-added technology products. Here are some examples of historical process innovations and how they illustrate the importance of learning by doing.
The Watt Process for power generation from steam: James Watt’s improvements to the steam engine in the 18th centry weren’t solely based on theoretical knowledge. He continuously experimented and refined his designs through practical application, gradually increasing the engine’s efficiency and paving the way for the Industrial Revolution.
The Bessemer Process for Steel Production: In the 19th century, Henry Bessemer developed a process for mass-producing steel. This involved blowing air tinto molten iron to remove impurities. While the initial concept was based on scientific principles, the actual implementation required extensive trial and error to perfect. The continuous refinement of the Bessemer process through practical experience led to a significant reduction in steel prices, fueling advancements in construction, transportation, and other industries.
The Planar Process for Microelectronics: Developed in the late 1950s, the plannar process revolutionized the manufacturing of transistors and integrated circuits. This method involved building layers of semiconductor material on a flat substrate. While the scientific understanding of semiconductor was essential, mastering the intricate steps of the planar process required practical experience and continuous improvement through learning by doing. This innovation enabled the miniaturization fo electronics and paved the way for the digital innovation wave.
Fordism: Pioneered by Henry Ford in the early 20th century, revolutionized manufacturing through mass production, vertical integration, experimentation and innovation (e.g. introduced the moving assembly line, a radical innovation that significantly accelerated production)
Theses cases emphasize that the United States must regain its learning by doing advantage in advanced manufacturing to compete effectively in the global technology landscape.
Value Chain
Business Model and Cultural transformation
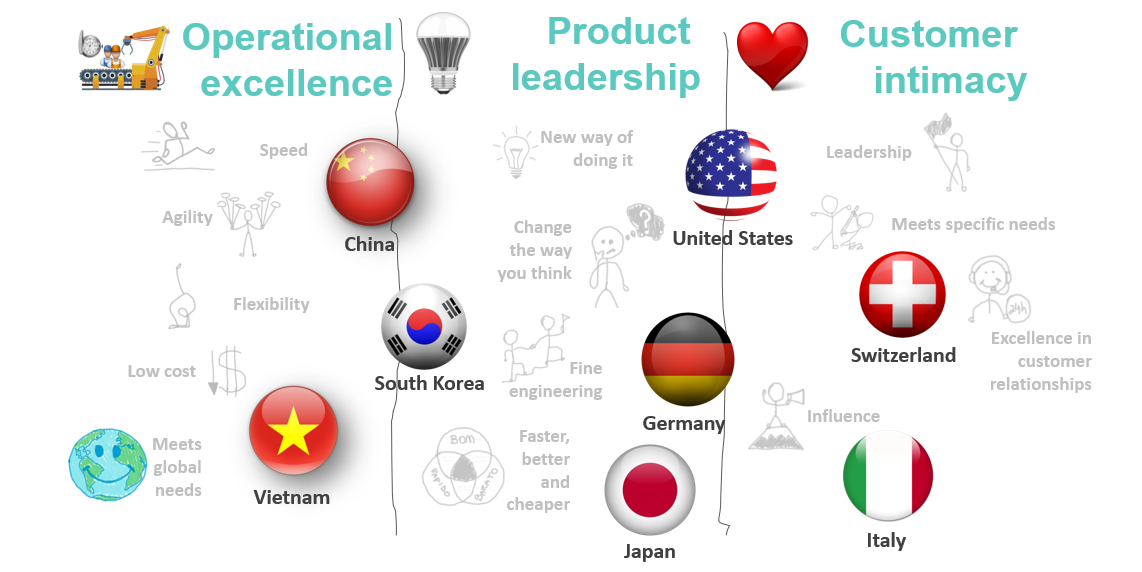
Acording Treacy and Wiersema (1993) to becoming an industry leader requires to choose a value discipline that takes into account its capabilities and culture as well as competitors’s strengths .
Redefined value, create new experiences and perception of benefit For example the value I got from this new electric vehicle.
Business systems that could deliver more of that value than competitors.
Raised customers’s expectations beyound the competition’s reach. Today’s customers have an expanded concept of value that includes convenience of purchase, after-sale service, dependability, and so on.
How to deliver superior customer value in line with one of the three value disciplines - operational excellence, customer intimacy or product leadership - in a world where populations are getting older Anjos (2024) , more urban, new tehnologies are emerging rapidly, economic activity in emerging markets is expanding rapidly all this without forgetting climate change ?

- What is relationship between small manufacturing and advanced manufacturing? (pag 24)
- What about capital access gaps for small medium manufacturing (pag 26)
- What about supply chain system with Allies and Partners (pag31,35)
- What about training and talent (pag 36, 37,38, 39) and Earl Murman(MIT) with japanese training stats, Ebbinghaus forgetting curve, Jereme Bruner, Lev Vygotsky, Richard Skemp, Zontan Deans, Jean Piaget, Denis Littly, and Raj Shaunak.
Workforce Education
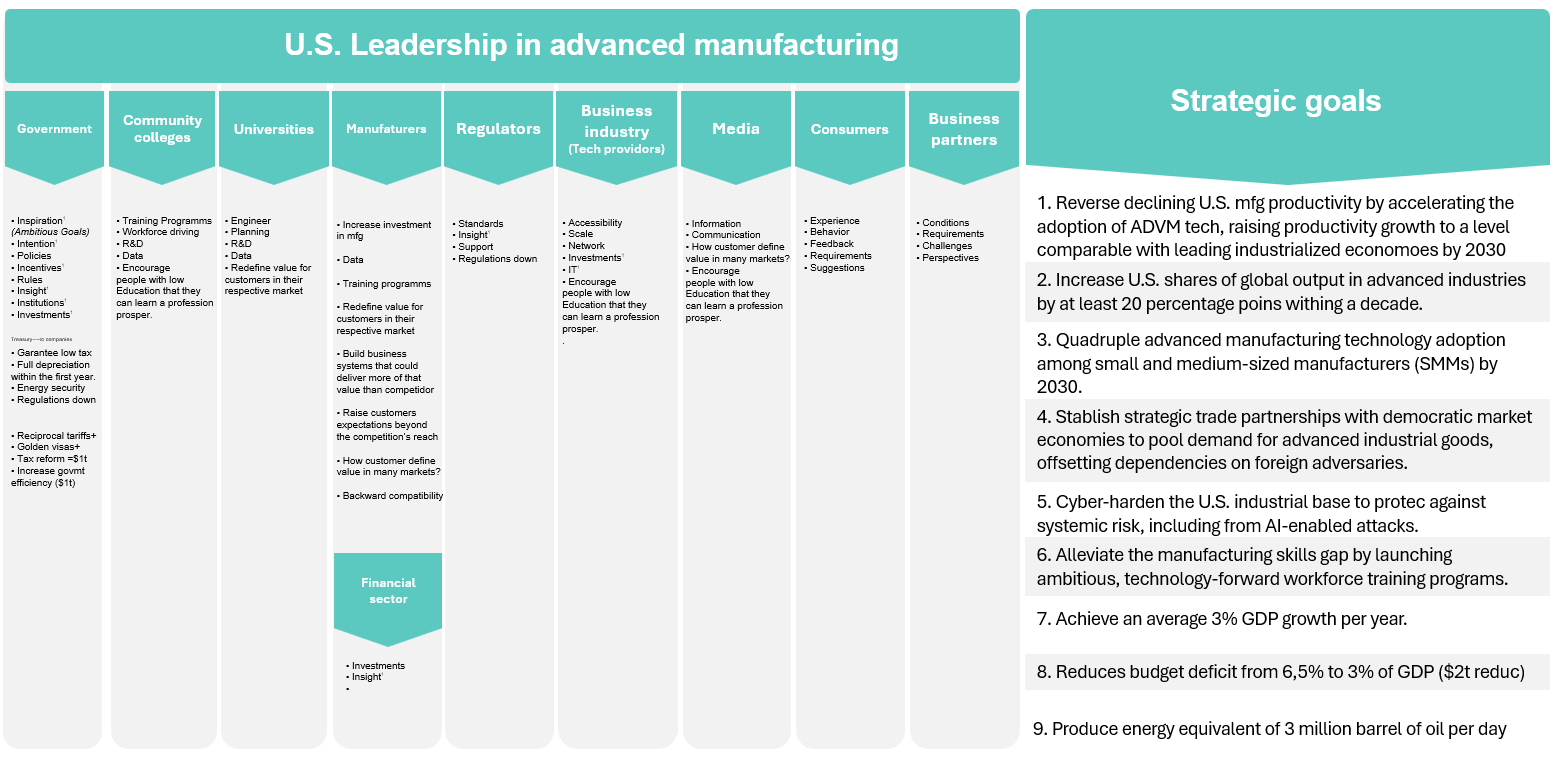
U.S. Strategy Goals
Reverse declining U.S. manufacturing productivity by accelerating the adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies To achieve productivity levels comparable to leading industrialized nations, the workforce must be trained in operating, maintaining, and innovating with technologies like AI, robotics, and digital twins. This requires widespread technical education, certification programs, and hands-on training in smart manufacturing systems.
Quadruple advanced manufacturing technology adoption among small and medium-sized manufacturers by 2030. SMMs often lack the resources to train staff in new technologies. Workforce education must include scalable, affordable training solutions such as online platforms, mobile labs, and regional training hubs to ensure these business can adopt and benefit from ADVM tools.
Establish strategic trade partnerships with democratic market economies to pool demand for advanced industrial goods. These partnerships will increase demand for high-quality, export-ready products, requiring a workforce skilled in international standards, quality assurance, and supply chain logistics. Education must include global trade literacy and cross-cultural communication skills.
Increase U.S. share of global output in advanced industries by at least 20 percentage poins within a decade. Competing globally in high-tech sectors demands a workforce proficient in STEM field(Science, Technology, Engineering, and mathematics), systems engineering, and digital production. Education systems must align with industry needs, emphasizing innovation, design thinking, and cross-disciplinary collaboration.
Cyber-harden the U.S. industrial base to protect against systemic risk, including from AI-enable attacks. As cyber threats grow, especially in AI-integrated systems, there is critical need for cybersecurity professionals with expertise in industrial control systems. Workforce development must prioritize cyber-physical security training and certifications tailored to manufacturing environments.
Produce energy equivalent to 3 million barrels of oil per day. Meeting this energy goal likely though renewables, nuclear, and advanced fuels requires a new generation of energy technicians, engineers, and systems operators. Workforce education must expand to include green energy technolgies, environmental systems, and energy policy literacy.
Reduce the budget deficit from 6.5% to 3% of GDP (a $2 trillion reduction). A more productive, higher-skilled workforce can increase tax revenues and reduce reliance on social safety nets. Education investments, particularly in high-return areas like technical training and adult reskilling, are essential to achieving fiscal sustainability.
Achieve an average 3% GDP growth per year. Sustained economic growth depends on labor productivity and innovation. Workforce education must foster entrepreneurial thinking, digital fluency, and adaptability to ensure workers can contribute to and benefit from a dynamic economy.
Workforce-Driven Economic Agenda
National strategy are influence industrial sectors and emphasizes the role of workforce development as a central driver of change. This change has significant implications for workforce development, particularly in traditional industries such as automotive, steel, textiles, and electronics.
These sectors, once the backbolne of American industry, are now being reimagined through the lens of advanced technolgy and sustainability. As a result, a new model of education and training is not just relevant, it’s essential.
Many of these legacy industries are undergoing technological modernization, incorporating robotics, the Internet of Things(IoT), and artifical intelligence(AI) into their operations. This transformation demands a workforce that is not only familiar with theses technologies but also capable of leveraging them to drive productivity and innovation. However, there is a growing skills gap between what workers currenly know and what modern manufacturing requires. Traditional vocational training programs often struggle to keep pace with the rapid evolution of technology, making them insufficient for preparing workers for the future.
At the same time, demographic shifts are creating additional pressure. As older workers retire, there is an urgent need to attract younger talent to these industries. A modernized, tech-integrated education model can help make these careers more appealing to a new generation. Moreover, strengthening domestic manufacturing is also a matter of national resilience and security. Reducing dependece of foreing supply chains requires a robust, skilled workforce that can support and sustain local production capailities.
Artifical intelligence can play a transformative role in this educational shift. One of its most powerful contributions is the ability to personalize learning. AI can analyze individual learning styles and skill levels to create customized training programs, making education more effective and engaging. It can also power simulations and virtual training environments that replicate complex industrial settings, allowing workers to train safely and efficiently without needing access to physical equipment.
Beyond training delivery, AI can help forecast future skill demands based on industry trends, enabling education institutions to proactively design curricula that meet emerging needs. It can also automate the creation and translation of traingin materials, makig educational more accessible to diverse populations.
Forging the Future
As the United States pursues ambitious industrial and economic goals for the coming decade, the need for actionable, context-aware recommendations becomes increasingly urgent. However, achieving these outcomes requires more than policy declarations, it demands a strategic rethinking of how we prepare workers for the evolving demands of twenty-first-century industries.
W. B. Bonvillian and Sarma (2021) present a compelling case for transforming the fragmented and outdated systems of workforce training in the U.S. They argue that the current model is ill-equipped to meet the pace of technological change and the scale of economic disruption. Their work highlights the importance of rapid, scalable, and inclusive education models such as short-cycle credentialing, modern appreniceships, and the integration of new learning technologies that can equip workers with the skills they need now, not just in the distant future.
Drawing from this framework, the recommendations that follow are grounded in situational knowledge: they respond to the specific challenges faced by key industrial sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and retail, and align with the strategic goals outlined for national growth and resilience. These proposals aim to bridge the gap between policy ambition and workforce readiness, offering pathways to empower individuals, strengthen industries, and ensure that technological progress translates into broad-based economic opportunity.
Short, Intensive Programs in Advanced Manufacturing
A significant need is anticipated in manufacturing sector, with an estimated two million or more manufacturing jobs opening in the coming decade due to an aging workforce and retirements. The sector requires a lot of upskilling to undertake advanced manufacturing and remain competitive, which means new hires will need higher skills.
Development of short course (10-20 weeks) as crucial new approach for the workforce, as many cannot take two years off for a degree. These programs should offer credentials that can be built into groups and stacked towards degrees over time.
Universities can contribute to developing new advanced curriculum for fields like advanced manufacturing.
Putting New Education Technologies to Use
Online education as a powerful thing and a game changer especially for scaling up to meet workforce training challenges.
Key technologies highlighted include augmented reality and virtual reality. Online credentialing is also critical, allowing individuals to earn verified digital credentials for short courses that can be easily shared(e.g linkedIn, Xjobs) and validated by employers without traditional verification calls. The MicroMasters program at MIT is an example of such a credentialing system, offering a pathway to a master’s degree.
The rapid pace of change, with new job category like data scientist and Instagram marketing emerging quickly, makes online education crucial for rapid retraining and upskilling. The science of learning principles, such as spaced retrieval (revisiting information over time) and interleaving(alternating topics to detect differences), are also better supported by online platforms.
For the future of education technology, Andrej Karpathy at Y Combinator (2025) spoke about the need for two distinct applications. One for teachers and one for students. This concept stems from his broader vision of software 3.0, where large language models and natural language interfaces redefine how we build and interact with software.
Karpathy argues that the roles of teachers and students are fundamentally different in the learning process, and therefore, their digital tools should reflect that distinction.
For students, the app should be optimized for exploration, engagement, and personalized learning. It would leverage AI to adapt content to each learner’s pace, style, and interests, offering interactive lessons, real-time feedback, and gamified experiences. The student app becomes a dynamic tutor, capable of guiding learner through complex topics using conversational interfaces and intelligence scaffolding.
For teachers, the app would serve as a command center for orchestrating learning experience. It would provide insights into studen progress, highlight areas where learners are struggling, and suggest interventions. Teachers coudl use it to design curricula, assign tasks, and even co-crate content with AI assistance. Importantly, this app would also support professional development, helping educators stay current with pedagogical strategies and technological tools.
Karpathy emphaisizes that separating these apps allows each to be deeply optimized for its user’s needs. Teachers require analytical and administrative capabilities, while students benefit from intuitive, immersive learning environmnet. By building these apps around the strengths of AI with natural langague undestanding, personalization, and automation, education can become more scalabe, inclusive, and effective.
Collaboration Between Federally Supported Programs
Unifying effort at the state level, reconnecting Labor Department and Education Department, enabling them to work in tandem and foster collaborative initiatives.
Robust and transparent labor market information system is essential to underpin an effective workforce education system. The current system leaving workers unsure of necessary skills, educators uncertain of what to teach and employers lacking clear information on available talent. Fixing this information gap is paramout for guiding all participants effectively.
Broader expanded employer role in workforce education. This includes employers engaging in disigning curriculum to ensure that training programs deliver the specific skills their workforces need. Programs like apprenticeship lite, co-ops, or internships are encouraged to break down the work-learn barrier, fostering coordinated efforts between educational institutions, employers, workers, and students.
Categories of job tasks
Frank Levy, along with David Autor and Richard Murnane, developed a framework for analyzing how technological change affects labor markets by classifying job tasks into five distinct categories. This classification helps explain which types of work are most susceptible to automation and which are likely to remain in human hands.
Routine Cognitive tasks These tasks involve mental processes taht follow well defined procedures and rules(e.g bookkeeping, data entry, and basic clerical work). Because they are rule-based and repetitive, they are highly susceptible to automation and offshoring. Computers and software can perform theses tasks efficiently, leading to a decline in demand for workers who specalize in them.
Routine manual tasks These tasks are physical activities that also follow predictable patterns(e.g. assembly line work, machine operation, and packaging). Like routine cognitive tasks, these are vulnerable to automation through robotics and mechanization. Their decline has been notable in manufacturing sectors where machines can replicate human actions with precision.
Non-Routine analytical tasks These tasks required problem-solving, critical thinking, and the application of spcialized knowledge(e.g. scientific research, engineering, financial analysis, and strategic planning). These tasks are less susceptible to automation because they involve abstract reasoning and adaptability. In fact, technology often complements these rolse by enhancing data analysis and decision-making capabilities.
Non-Routine Interpersonal Tasks These tasks rely on human interaction, emotional intelligence, and communication skills(e.g. teaching, counseling, sales, and management). They are difficult to automate because they require nuance undestanding of human behavior, persuasion, and empathy. As service-oriented sectors grow, demand for these skills continue to rise.
Non-Routine manual tasks These tasks involve physical activities that are not easily codified or replicated by machines(e.g. cleaning, cooking, driving in unpredictable environments, and caregiving).While some aspects can be assisted by technologym, the complexity and variability of these tasks make full automation challenging. They often require dexterity, situational awareness, and adaptability.
Healthcare and Social Assistance
This is the largest employment sector in the U.S. with over 23.3 million workers. It accounts for approximately 13.9% of the total U.S. labor force, which stands at around 167.8 million. The sector continues to grow due to aging demographis and increasing demand for health services.
Retail Trade
Retail employs about 15.2 million workers, making up roughly 9.1% of the total workforce. While still a major employer, the sector has seen slight declines due to e-commerce and automation in logistics and customer service.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing employs approximately 12.75 million workers, representng around 7.6% of the labor force. Though smalller than the other two, it remains vital for economic output and national infrastructure.
SMEs & Information Systems
History of SME here
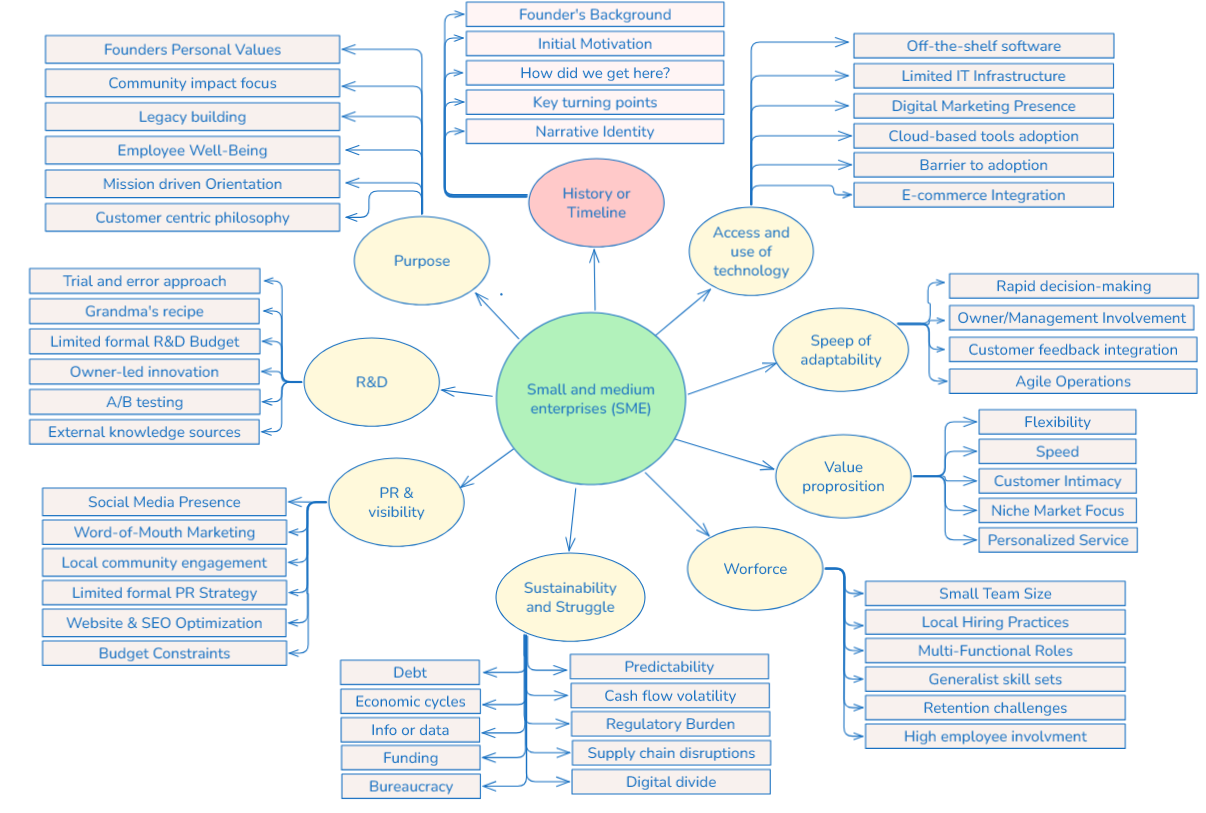
Manufacturing-focus Approach
The U.S. advanced manufacturing plan, as outlined in resources like manufacturing.gov, aims to increase productivity, improve supply chains, and retain a strong workforce.
Shift Focus from Design to Manufacturing
The U.S. must recognize that while innovation in product design is important, the real competitive advantage lies in mastering manufacturing processes. This means investing heavily in research and development of manufacturing technologies, such as advanced robotics, AI-driven quality control, and sustainable production methods.
“Manufacturing is underrated and design overrated”. This suggests that the initial design of a product, such as a rocket engine, is just the beginning. The real challenge lies in scaling that design into a manufacturable, cost-effective, and reliable, product.
The effort to design a manufacturing system is exponentially greater than the effort to design the product. For instance, that designing the Raptor engine required significantly less effort compared to designing the manufacturing system to produce it at scale. This is because manufacturing involves not just producing one unit but thousands, each with consistent quality and at a reduced cost.
Embrace Vertical Integration
To reduce vulnerability to global supply chain disruptions and improve control over production quality, the U.S. should encourage policies that support vertical integration. This could involve incentives for companies to bring manufacturing back to the U.S. or to develop domestic supplier networks. The National Strategy for Advanced Manufacturing should prioritize building a robust ecosystem that supports end-to-end production.
SpaceX’s success is partly due to its vertical integration strategy, where the company controls most aspects of production, from raw materials to final assembly. This approach reduces dependency on external suppliers, improves quality control, and lowers costs. Musk’s emphasis on process engineering means optimizing every step of the manufacturing process, from supply chain logistics to automation, to ensure efficiency and scalability.
Invest in Workforce Training for Manufacturing
The U.S. must invest in training programs that focus on advanced manufacturing skills, such as process engineering, automation, and data analytics. Programs like apprenticeships, community college partnerships, and industry-led training initiatives can bridge the skills gap.
Prioritize Cost Efficiency and Scalability
U.S. manufacturers need to adopt a cost-conscious approach, where design constraints include economic viability at scale. This might involve rethinking traditional manufacturing paradigms to incorporate modular designs, additive manufacturing(3D printing), and other techonologies that reduce waste and increate flexibility.
A critical aspect of SpaceX approach is desgning with cost in mind from the outset. They challenges the team to achieve a cost per ton of thrust under $1000 for the Raptor engine, which is a formidable constraint that drives innovation in both design and manufacturing. This cost-focused approach is not just about cutting expenses but about reimagining how products are made to be economically viable at scale.
SpaceX advocates for accelerating cycle times but only after ensuring the design and process are optimized. This iterative approach allows for continuous improvement and adaptation, which is crucial in high-stakes industries like aerospace where failure is not an option.
Leverage Data and Automation
The future of manufacturing is digital, and the U.S. must lead in adopting Industry 4.0 technologies. This includes IoT(Internet of Things) for real-time monitoring, AI for predictive maintenance, and advanced robotics for precision manufacturing. These technolgies can significantly reduce cycle times and improve quality.
Policy Support for Innovation in Manufacturing Processes
The U.S. government should provide incentives for innovation in manufacturing processes, not just product design. This could include tax breaks for companies that invest in new manufacturing technologies, grants for research into process optimization, and regulatory support for pilot projects that test new manufacturing methodologies.
Collaborative Ecosystems
Building collaborative ecosystems where academia, industry, and government work together can foste innovation in manufacturing. Universities can develop curricula focused on manufacturing engineering, industry can provide real-world applications, and goverment can fund initiatives that bridge the gap between theory and practice.
Skills Requirements
Skills requirements refers the abilities workers need and the specific content that workforce education must cover to ensure they develop those skills. A set of training competency categories that outline the essential knowledge and abilities required in modern workplace education had been created by the U.S. Department of Labor.
- Personal Skills refer to the basic behaviors and attitudes that individuals bring to any job, such as reliability, lifelong learnin, self-management, communication, and professionalism. Their main purpose is to ensure that workers can behave responsibly, interact well with others, and manage themselves efffectively in any work environment.
Summary Workforce education studies by Merrilea Mayo pag 168.(key personal and interpersonal skills set out by employers)
Critical thinking is the ability to analyze information carefully, question assumptions, and make sound judgments. It helps individuals solve problems more effectively and make better decisions in both independent and collaborative work.
Works independentlyrefers to the capacity to manage one’s own tasks without constant supervision, staying organized, focused, and accountable for results. It reflects maturity and realiability in any professional setting.
Collaboration and teamwork involve working productively with others, communication clearly, listening actively, and contributin to shared goals. This skill ensures that individuals can integrate diverse perspectives and maintain positive group dynamics.
Grit and mindset relate to perseverance, resilience, and the belief that abilities can grow through effort. They help people staty motivated and overcome setbacks, especially when facing long-term or difficult challenges.
Time management is the hability to prioritize tasks, plan ahead, and use available time efficiently. It supports productivity and reduces stress by allowing individuals to meet deadlines and maintain steady progress.
Curiosity reflects a desire to learn, explore new ideas, and ask meaningful questions. It fuels continuous improvement and helps people adapt to changing environments.
Creativity is the skill of generating original ideas, seeing alternative solutions, and approaching problems from fresh angles. It encourages innovation and contributes to better problem-solving in both technical and interpersonal settings.
Openness describes the willingness to consider new perspectives, accept feedback, and adapt to new situations or ways of thinking. It makes individuals more flexible and receptive in diverse workplaces.
Motivation refers to the internall drive that pushes someone to act, learn, and achieve. It sustains effort over time and supports engagement, productivity, and overall performance.
Academic competencies involve foundation knowledge learned through formal education, including reading, writing, math, science, digital literacy, and critical thinking. These competencies exist to give workers the analytical abilities necessary to understand information, follow instructions, and solve problems in increasingly complex workplaces.
Workplace competencies focus on the practical abilities needed to function efficiently within an organization. They include teamwork, problem-solving, adaptability, planning, and the use of workplace technologies. The goal is to prepare workkers to contribute productively within teams, handle day-to-day taks, and operate within real organizational systems.
Industry-wide technical competencies represent the technical knowledge that applies broadly across and entire sector, such as manufacturing, healthcare, or logistics. These skills ensure that workers understand common tools, processes, safety requirements, and regulatory expectations that define performance and quality across the industry.
Occupational-specific technical competencies refer to the specialized abilities required for a particular job role. These competencies are tied directly to specific tasks, technologies, and procedures unique to a given occupation. Their goal is to make sure that workkers can perform the specialized, technocal functions of their role at a high level of accuracy, productivity, and safety.
Case study Workkeys at Phifer in Tuscaloosa pag 161. They have achieved program completion rates that range from 61% to 87% across schools, and job placement rates from 76% to 92%. $2 million reduction in training costs, a 25% cut in training time, a 40% improvement in the quality of applicant, a 33% reduction in orientation time, and a 15% increase in workforce punctuality.
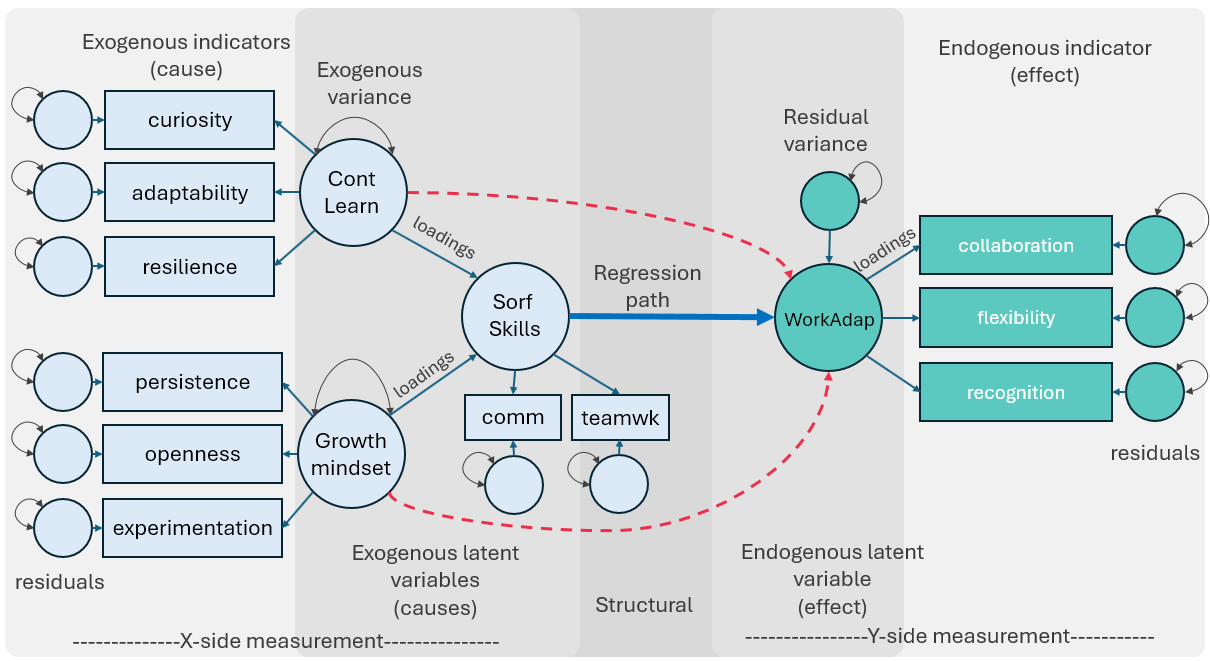
Modeling Workplace Adaptation
Workplace Adjustement: A Theoretical Approach