Data-Driven Lean Manufacturing
What concepts and practices are involved in this process?
Lean Principles
The basic idea of Lean principles is to focus on the customer value that requires a smooth flow in production and elimination of waste during the value-adding process. The quality is built into every step (e.g design, engineering, production, shipping) making it more adaptable to changing environment, and improvement is driven by workers. One example of value is how much the customer is willing to pay for something.
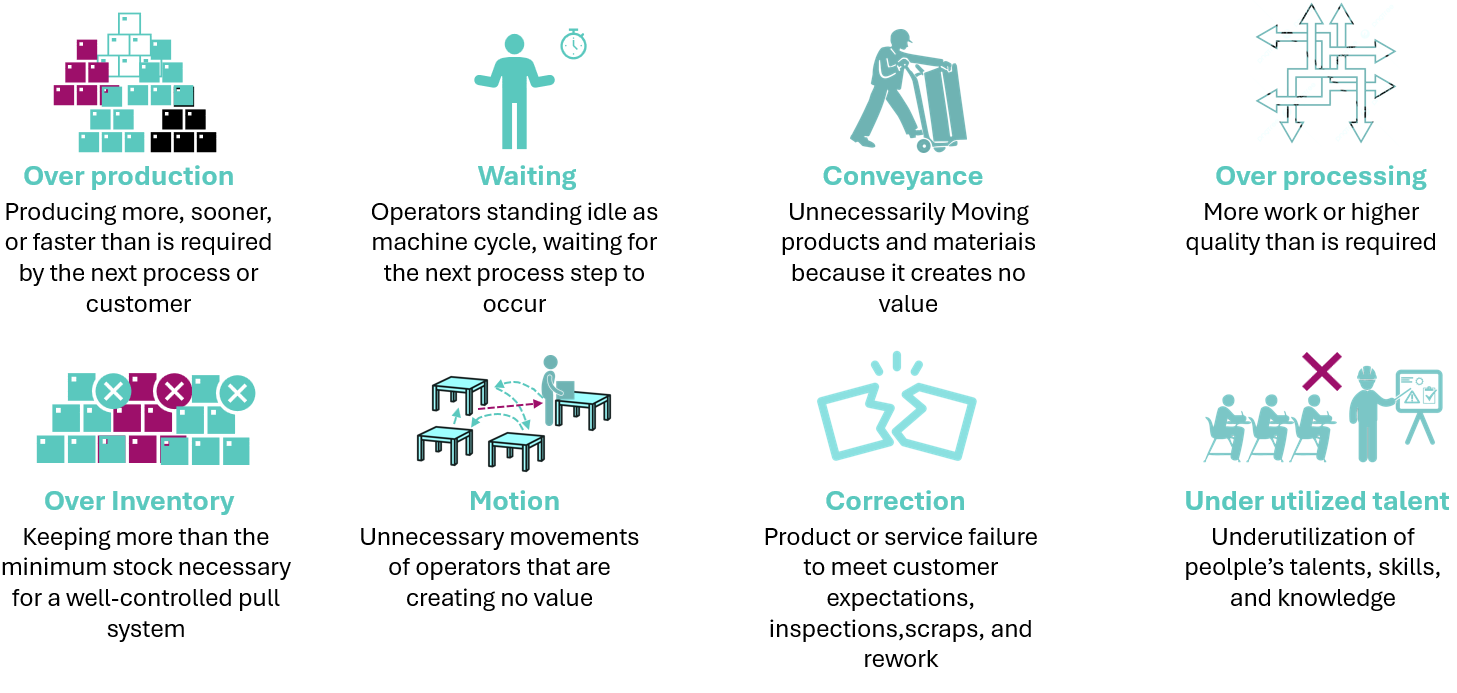
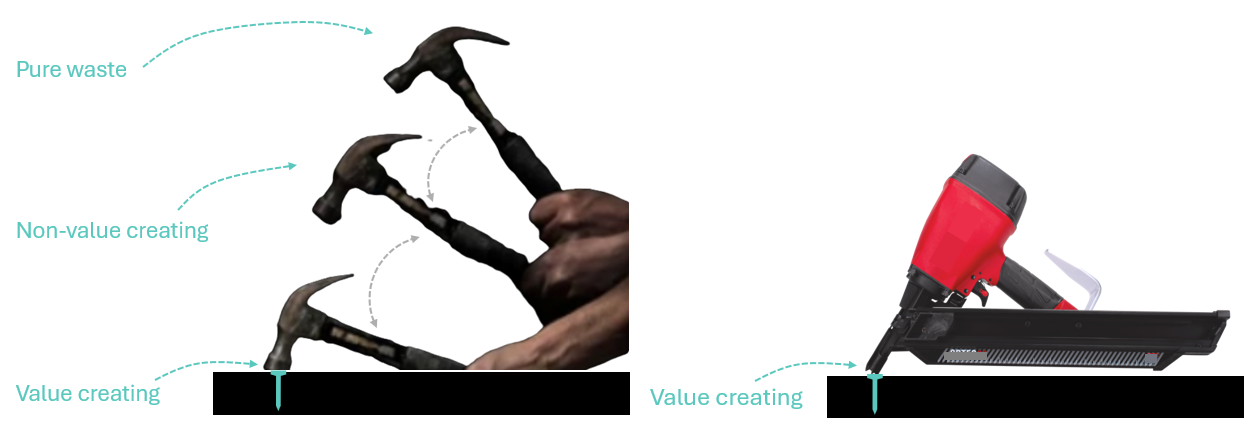
Value-added activity: transforms or shape materials, and the customer wants it
Non-value added activity necessary waste: No value is created, but cannot be eliminated based on current technology, policy or thinking for example regulatory procedures, inspections, invoices etc.
Non-value added activity pure waste: No value is created and consumes resources for example inventory, rework, excess steps and checks, accidents, scraps, waiting times.
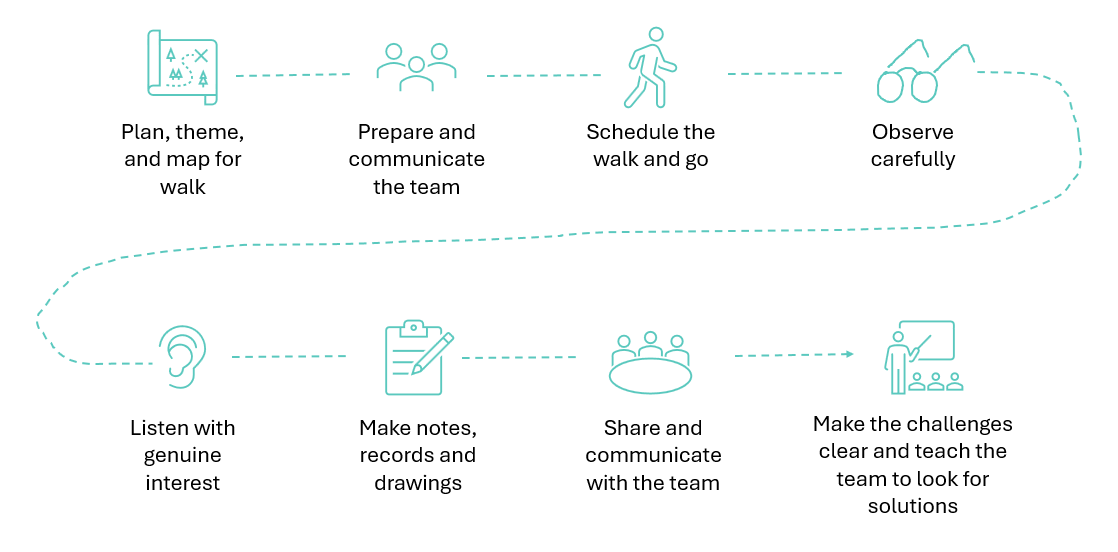
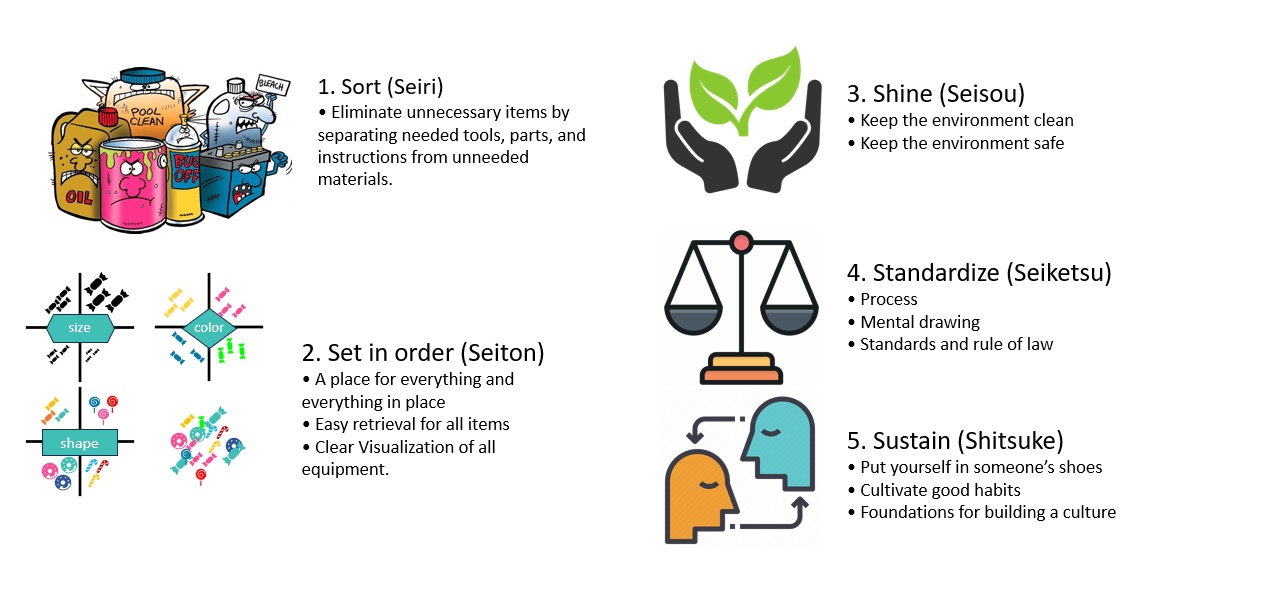
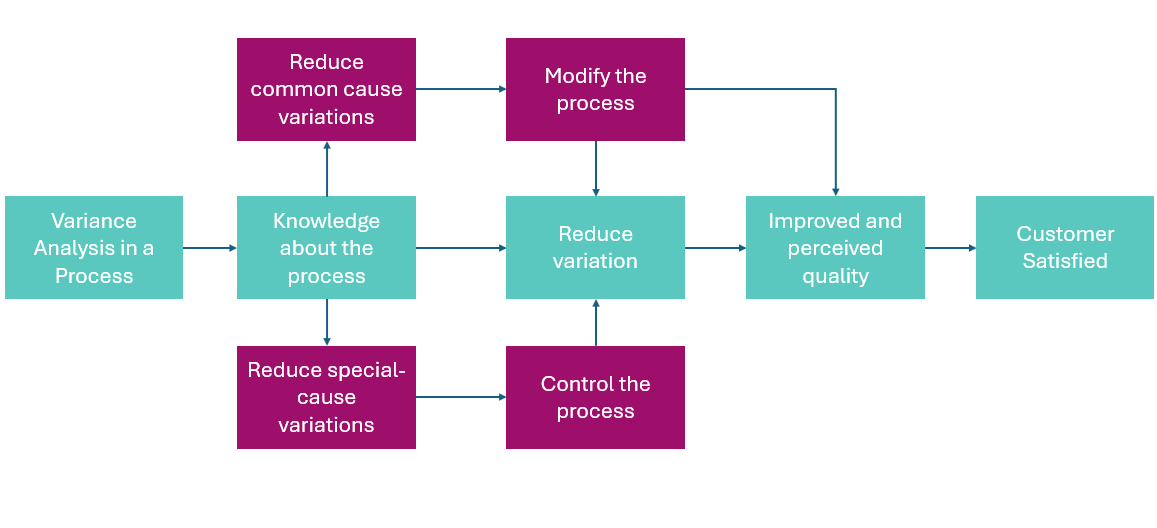
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence encompasses a powerful set of general-purpose tools. These include machine learning models used for prediction and recomendation, large language models that support knowledge dissemination and tasks automation, computer vision systems that enable the capture, processing, and control of manufacturing operactions, digital twins that simulate virtual environments using real-time data, and autonomous agents capable of performing tasks in produtions settings.
To make these technologies work effectively, several key components are required such as labeled and synthetic data, sensors, variation control, optimization techniques, engineering, design, and many other elements developed by humans.
Since our focus is on manufacturing, we continue with the following questions:
How can AI tools(e.g., predictive, generative, and agent-based models) support the implementation of a lean culture in business?
How can Lean principles, the PDCA method, and quality tools be integrated into an AI agent to effectively solve manufacturing problems?
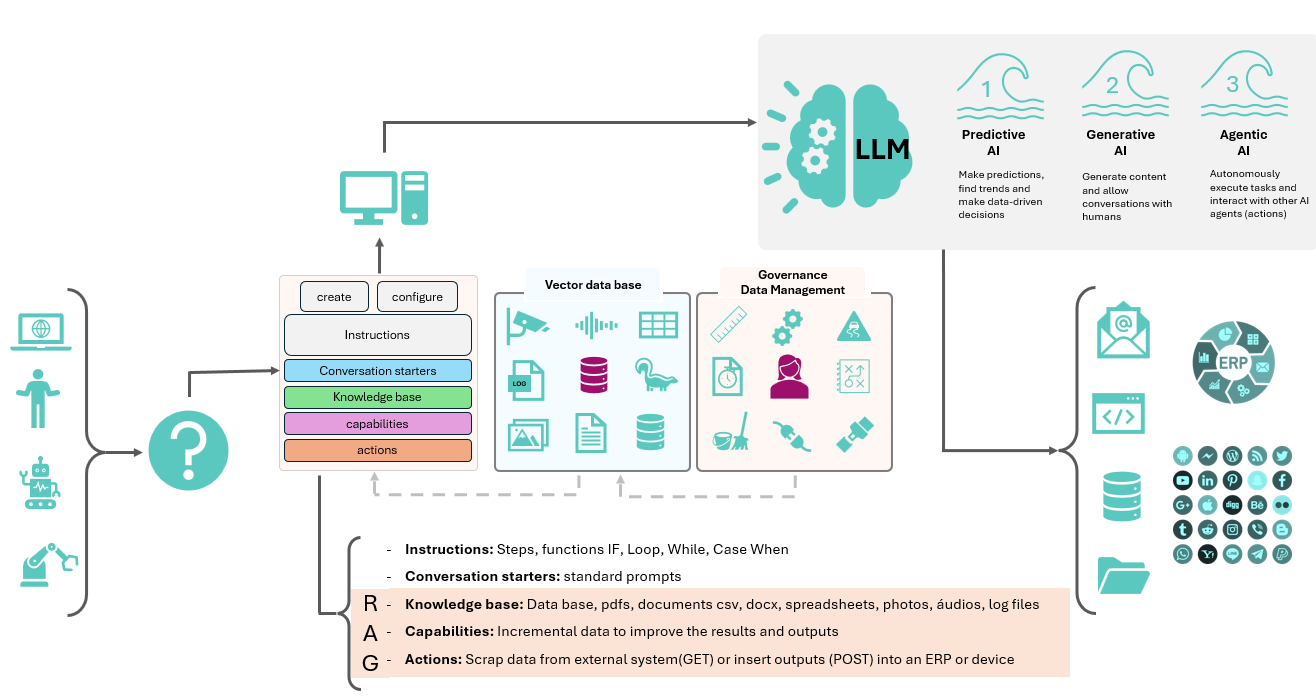
An example of te retrieval-agumented generation(RAG) approach, which leverages a knowledge base as contextual input to enhance the performance of large language models(LLMs).
PDCA
The basic idea of PDCA method is create a universal language to serve as a guide for thinking during the problem-solving process. If language is the vehicle of thought Wittgenstein and Monk (2022), PDCA is a way to make that vehicle faster.
The basic idea of the quality tools is reduce waste during performing a value-added task or process, for example time, effort, unnecessary movement etc.
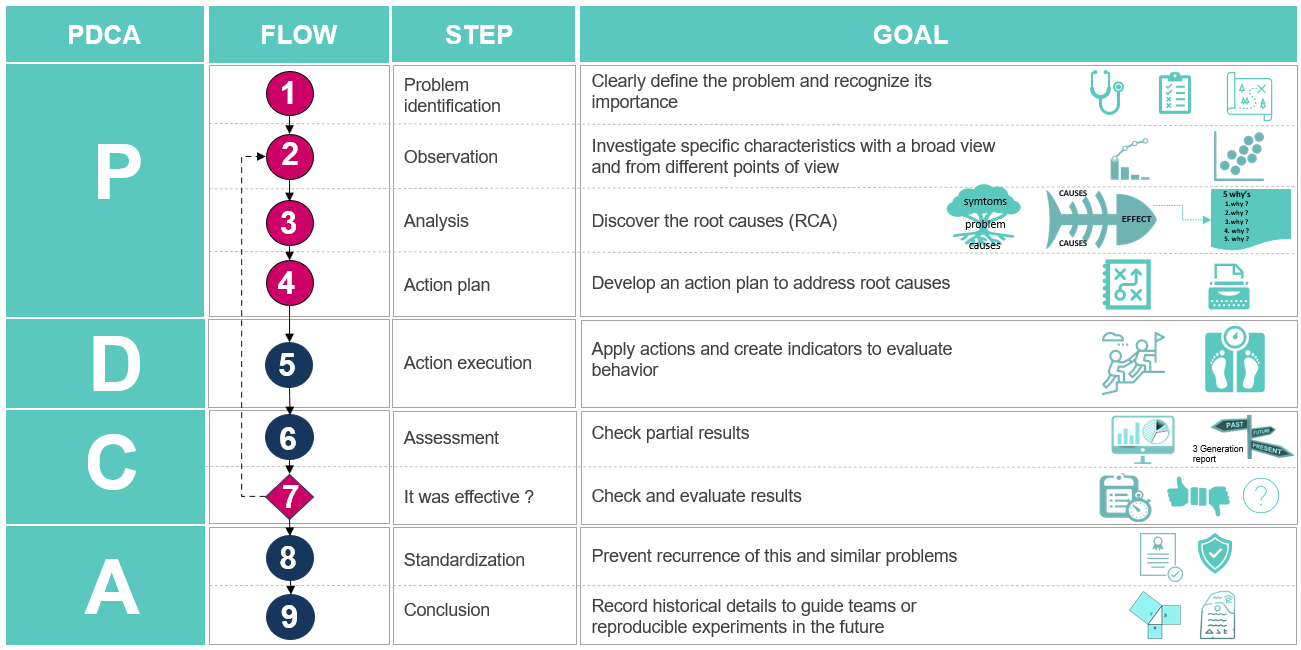
PDCA (Plan-do-check-action) Method
Data Science
Data science is the practice of solving real-world problems using data to create meaningful impact for a business or system. This impact can take the form of insights, data products, or actionable recommendations. To achieve this, data scientists rely on tools such as machine learning models, data visualizations, technical reports, dashboards, and more.
The principles of data science involve breaking down complex problems into fundamental truths, collecting data from diverse sources, and identifying and correctiong errors and inconsistencies to ensure data quality. Data is then analyzed(visually and statistically) to uncover patters and insights. This process includes transforming and selecting variables, and applying techniques such as statistics, programming, and machine learning to build various types of models:
- Descriptive models, which help illustrate and summarize the characteristics of the data.
- Inferential models, which support decision-making by answering research questions or testing specific hypotheses.
- Predictive models, which aim to generate the most accurate forecasts possible for new or unseen data Kuhn and Silge (2022).
Among the foundations of data science, two stand out as fundamental:
Scientific, which would basically be asking “why” and demanding a rational answer to que question. It requires abilities such as ask insightful questions, active listening, strong orgazational skills, and effective communication of complex ideas in simple terms. As data science often involves sensitive information, understanding ethical considerations and data privacy is critical. This ensures that data is used responsibly and in compliance with regulations.
Technical, which would basically the application of technical or scientific knowledge or both to something with a practical purpose. it requires abilities in statistics and probability such as data distributions and statistical tests, programming like Python and R, ability to represent data visually for communicating findings, and machine learning that involves training models to make predictions or decisions based on data.
Today, advanced sensors, IoT devices, and AI-driven analytics enable real-time monitoring of production lines, predictive maintenance, and quality control. Machine learing algorithms help in identifying patterns and anomalies, leading to proactive decision-making.
Looking forward, autonomous decision-making, adaptive manufacturing systems, and personalized production will coexist. Data integration across supply chains and the adoption of digital twins will enable virtual simulations for testing and optimization before physical production begins. Use of cyber-physical systems will reduce the boundaries between the physical and digital, with smart-manufacturings capable of self-otimization, atomic-level vision capability and real-time response to market demand. Some examples os pratical application os data science on manufacturing including:
Predictive Analysis: To monitor businesss operations, performance, and potential solutions to problems impeding future prospects. Machine learning and deep learning are used to predict energy consumption, mechanical properties, and other performance metrics.
Maintenace: Predict equipment failures, enabling manufacturers to take proactive measures to avoid or mitigate them. By leveraging predictive analytics techniques, manufaturers can identify potential issues before they occur, reducing downtime and increasing overall efficiency. Traditional time-based preventative maintenance strategies can be augmented with data-driven insights, allowing for more informed decision-making and optimized maintenance planning. With careful planning and analysis, equipment manufacturers can schedule maintenance breaks or shutdowns to address potential problems, minimizing delays and failures. This proactive approach helps ensure equipment reliability, reduces maintenance costs and optimizes production output.
Price reduction: To optimize their pricing strategies, leading to significant cost reductions. When setting product prices, manufaturers must consider a multitude of factors, including raw material costs, manufacturing expenses, distribution fees, maintenance costs, and more. To strike the perfect balance between profitability and customer affordability, manufacturers leverage price optimization techniques. By analyzing pricing and cost data from both internal and external sources, data science anables manufaturers to gain a competitive edge and develop optimized price variants. This data-driven approach allows manufacturers to identify areas of inefficiency, minimize costs, and maximize revenue, ultimately leading to increased profitability and a stronger market presence. Manufacturers can make informed pricing decisions that drive business growth, improve profitability, ad enhance customer satisfaction.
Directing the Supply Chain: Data science could help manufaturers to navigate risks and uncertainties, providing visibility with the agility they need to respond quickly to changing market conditions and customer needs. Proactively identify potential disruptions, asses their likelihood, and develop strategies to mitigate their impact. Supply chain management requires a deep understanding of the complex variables, including supplier performance, inventory levels, transportation costs, and customer demand. Some examples where data science can be helpful in the supply chain are shown below.
Warranty Analysis: To optimize warranty claims process by analizing data from various sources, including product performance, customer feedback, and warranty claims, manufaturers can identify early warning signs for product failures and take proactive measures to address them. Data scientists can help manufacturers analyze the root causes of product defects, identify patterns and trends, and develop predictive models to forecast potential warranty claims. With the help of AI and warranty analytics, manufacturers can process vast amounts of warranty-related data from multiple sources, including:
Product Authenticity: Product authenticity is particularly important in the pharmaceutical and food industries, where counterfeit or adulterated products can have serious consequences for public health. Near Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) is a powerfil analytical technique to help manufacturers to ensuring the authenticity of products across various industries. With the unique spectral signatures of materials, NIRS enables the rapid and non-invasive identification of chemical composition, allowing manufacturers to verify the ahthenticity of their products. The system operates by emitting infrared photons from the light source, which interact with the sample, causing molecular vibrations or stretching within the sample. These interactions result in a spectrum that reflects the properties of the molecules and thei chemical bonds. To extract meaningful information, the spectra undergo specific preprocessing (e.g. PLS,PCA) techniques to eliminate noise and redundat data. Subsequently, these techniques are employed to identify effective wavelengths that precisely classify the product.A well-constructed model can accurately classify the product with minimal error.
Robotization and Automation: To perform repetitive, mundane, and hazardous tasks, freeing up human workers to focus on higher-value activities. However, the integration and maintenance of robots can be a significant annual expense for manufaturers. This where data science comes in - by analyzing data from various sources(Exploring more in this topic in the future), manufacturers can optimize robot programming and operation, leading to improved product quality and reduced costs. Some examples of the pratical application of data science in robotis and